- BuildMaster
- Getting Started with BuildMaster
- Builds and Continuous Integration
- What is a "Build" in BuildMaster?
- Git and Source Control
- Git Pipelines and Workflows
- Build Scripts & Templates
- Packages & Dependencies
- Build Artifacts
- Automated Testing & Verification
- Deployment & Continuous Delivery
- What is a “Pipeline” in BuildMaster?
- CI Server (Jenkins, TeamCity, etc.) Integration
- Deployment Scripts & Templates
- Automatic Checks & Approval Gates
- Manual Deployment Steps and Tasks
- Databases
- Configuration Files
- Rollbacks
- Advanced CD Patterns
- Applications & Releases
- Connecting to your Servers with BuildMaster
- Scripting in BuildMaster
- Configuring for Your Team
- Docker/Containers
- Development Platforms
- Deployment Targets
- Tools & Service Integrations
- Reference
- BuildMaster API Endpoints & Methods
- Extending BuildMaster
- Built-in Functions & Variables
- Applications
- Builds
- Configuration Files
- Containers
- Credentials
- Databases
- Environments
- Executions
- Files
- General
- JSON
- Linux
- Lists
- Maps
- Math
- Nuget
- Packages
- Pipelines
- PowerShell
- Python
- Releases
- Servers
- Strings
- XML
- Built-in Operations
- Batch
- BuildMaster
- Configuration Files
- Databases
- DotNet
- Files
- Firewall
- General
- Apply-Template
- Attach Package
- Build
- Checkout-Code
- Close-Issue
- Concatenate-Files
- Copy-Files
- Create-Directory
- Create-File
- Create-Issue
- Create-Issue
- Create-IssueComment
- Create-Package
- Create-ZipFile
- Delete-Files
- Download-Asset
- Download-Http
- Ensure-Directory
- Ensure-File
- Ensure-HostsEntry
- Ensure-Metadata
- Ensure-Milestone
- Ensure-Package
- Ensure-Release
- Ensure-Tag
- Exec
- Execute Python Script
- Execute VSTest Tests
- Get-Http
- Install-Package
- OSCall
- OSExec
- Post-Http
- Push-PackageFile
- PYCall
- PYEnsure
- Query-Package
- Remediate-Drift
- Rename-File
- Repackage
- Replace-Text
- Send-Email
- Set-FileAttributes
- Set-Variable
- SHEnsure
- Sleep
- Transfer-Files
- Transition-Issues
- Upload-Assets
- Upload-Http
- Upload-ReleaseAssets
- Git
- IIS
- Nuget
- PowerShell
- ProGet
- Python
- Registry
- Servers
- Services
- Shell
- Windows
- Administration
- Installation & Upgrading
- ProGet
- Getting Started with ProGet
- Packages: Managing & Tracking
- Feeds Types & Third-Party Packages
- What is a "Feed" in ProGet?
- What is a "Connector" in ProGet?
- NuGet (.NET)
- Universal Feeds & Packages
- PowerShell
- Chocolatey (Windows/Machine)
- RubyGems (ruby)
- Visual Studio Extension (.vsix)
- Maven (Java)
- npm (Node.js)
- Bower (JavaScript)
- Debian (Apt)
- Helm (Kubernetes)
- PyPI (Python)
- Conda (Python)
- RPM (Yum)
- Alpine (APK)
- CRAN (R)
- pub (Dart/Flutter)
- Cargo (Rust)
- Terraform Modules
- Conan (C++)
- Composer (PHP)
- Other Feed Types
- Asset Directories & File Storage
- Docker and Containers
- Replication & Feed Mirroring
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
- Security and Access Controls
- Cloud Storage
- Administration
- Installation & Upgrading
- API Methods and CLI Commands
- Otter
- Getting Started with Otter
- Orchestration & Server Automation
- Connecting to your Servers with Otter
- Collecting & Verifying Configuration
- Drift Remediation / Configuration as Code
- Scripting in Otter
- Configuring for Your Team
- Installation & Upgrading
- Administration & Maintenance
- Reference
- Otter API Reference
- OtterScript Reference
- Built-in Functions & Variables
- Executions
- Files
- General
- JSON
- Linux
- Lists
- Maps
- Math
- PowerShell
- Python
- Servers
- Strings
- XML
- Built-in Operations
- Batch
- Docker
- DotNet
- Files
- Firewall
- General
- Apply-Template
- Collect Debian Packages
- Collect RPM Packages
- Collect-InstalledPackages
- Concatenate-Files
- Copy-Files
- Create-Directory
- Create-File
- Create-Package
- Create-ZipFile
- Delete-Files
- Download-Asset
- Download-Http
- Ensure-Directory
- Ensure-File
- Ensure-HostsEntry
- Ensure-Metadata
- Ensure-Package
- Exec
- Execute Python Script
- Get-Http
- Install-Package
- OSCall
- OSExec
- Post-Http
- Push-PackageFile
- PYCall
- PYEnsure
- Query-Package
- Remediate-Drift
- Rename-File
- Repackage
- Replace-Text
- Send-Email
- Set-FileAttributes
- Set-Variable
- SHEnsure
- Sleep
- Transfer-Files
- Upload-Assets
- Upload-Http
- IIS
- Otter
- PowerShell
- ProGet
- Python
- Registry
- Servers
- Services
- Shell
- Windows
- Installation & Maintenance
- Windows (Inedo Hub)
- Linux (Docker)
- High Availability & Load Balancing
- User Directories & Domains (LDAP)
- Logging & Analytics
- SAML Authentication
- When to Upgrade your Inedo Product
- Managing Agents and Servers
- Backing Up & Restoring
- Installation Configuration Files
- PostgreSQL & Inedo Products
- SQL Server & Inedo Products
- Inedo Agent
- What is the Inedo Agent?
- Installation & Upgrading
- Downloads & Release Notes
- Maintenance & Configuration
- Internal Architecture
- MyInedo
- OtterScript (Execution Engine)
- Reference
- OtterScript
- Inedo Execution Engine
- Romp (Discontinued)
- Using Romp
- Installing, Configuring, and Maintaining
- Romp CLI Reference
- Package Layout
- Downloads & Source Code
- Extensibility
- Inedo SDK
RPM (Yum)
RPM Package Manager (RPM, originally Red Hat Package Manager), is a free, open-source package management system used by many Linux distributions including Red Hat and CentOS. RPM packages can be hosted and installed from ProGet.
Prerequisite Configuration
In order to install packages from ProGet, each client must perform the following steps:
Add a .repo file to /etc/yum.repos.d
Yum stores its repository configuration in .repo files located in /etc/yum.repos.d/. To register a ProGet feed as a repository, create a new «repo-name».repo file in that directory with content:
[«repo-name»]
name=«repo-name»
baseurl=http://«proget-url»/rpm/«feed-name»/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
Note that «repo-name» can be anything, but we recommend using the ProGet feed name for clarity.
Verify yum configuration
To verify that Yum is able to download package metadata, execute:
$ yum repolist all
If the configuration is correct, this will list all repos (including the ProGet feed registered in Step 1).
Installing Packages
RPM packages are installed using Yum. To install a package hosted by ProGet, use the command:
yum install «package-name»
Creating and Publishing Packages
To learn how to create and publish an RPM package to ProGet, see our guide on HOWTO: Publish RPM Packages to a Private Repository in ProGet.
Connectors for RPM (Yum) Feeds
Starting in ProGet 2023.22, RPM (Yum) feeds support connectors to other ProGet RPM (Yum) feeds, official RPM repositories, and other third-party repositories.
When connecting to an official RPM repository, ProGet will periodically download the index file. To add a connector, follow our guide on HOWTO: Aggregate RPM Repositories in ProGet
When creating a connector to an official repository, we recommend using a name that follows the URL conventions. For example:
| URL: | https://mirror.stream.centos.org/9-stream/BaseOS/x86_64/os/ |
| Connector name: | centos-9-stream-baseos-x86_64-os |
You can see a list of the default repositories in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory on a new installation.
Authenticating to RPM (Yum) Feeds
By default feeds do not require authentication and can be viewed anonymously. However, you can configure it to require authentication to access. For example, when creating feeds to host your own internal packages.
First you will need to create an API key in ProGet. You can read more about this on our API Key page. When creating an API Key, fill in the fields by selecting "Feeds ("Use Certain Feeds)" as the "Feed Type" and selecting the RPM feed to authenticate to. Make sure that the required permission boxes are checked, and then select "Save".
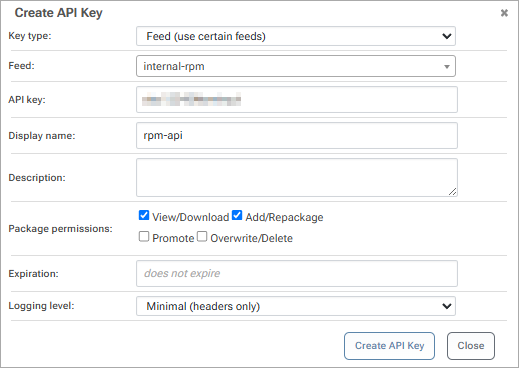
Alternatively you can create a "Personal API Key", which lets users create/delete API keys that are tied to their username.
Then add the feed to your local RPM environment which will require the RPM feed URL and API key. When editing the .repo file, enter your API key and URL in the baseurl parameter:
baseurl=http://api:«api-key»@«feed-url»
For example when authenticating with the API key abc12345 to the RPM feed URL http://proget.corp.local/rpm/internal-rpm/, your .repo file should look like this:
[internal-rpm]
name=internal-rpm
baseurl=http://api:abc12345@proget.corp.local/rpm/internal-rpm/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0

