HTTP Request Logging
Beginning with ProGet 2025.11, the Integrated Web Server now supports W3C HTTP Request logging. By enabling HTTP Request logging, ProGet will log all HTTP request information to a log file in the W3C Extended Log File Format. This log file can be used for auditing, monitoring, and troubleshooting purposes.
Enabling HTTP Request Logging
Enabling on Windows
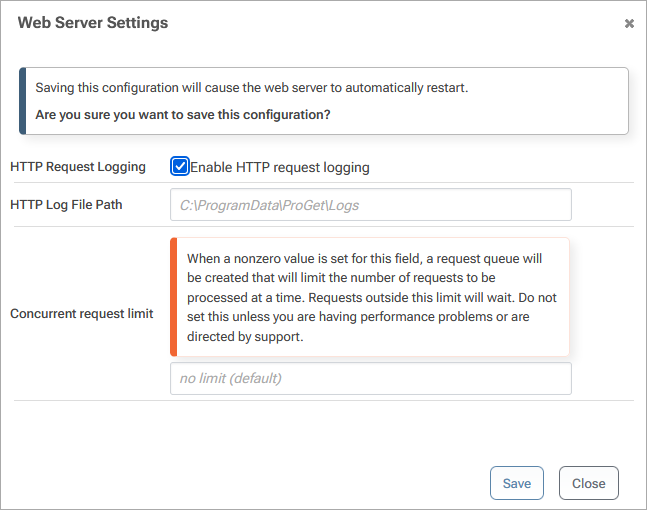
To enable HTTP Request logging in Inedo products on Windows, navigate to Administration -> HTTP/S & Certificate Settings and then click the "edit" button in the "Web Server Configuration" section. In the dialog that appears, check the "Enable HTTP Request Logging" checkbox and then click "Save". By default, the log files will be stored in C:\ProgramData\ProGet\Logs on Windows, but you can change this by modifying the HTTP Log File Path field.
Enabling on Docker
To enable HTTP Request logging in Inedo products on Docker, you will need to add the ENABLE_REQUEST_LOGGING environment variable and set it to true (ex: -e ENABLE_REQUEST_LOGGING='true'). Once enabled, HTTP Request logs will be saved to /var/«inedo-product»/logs within the container. For these logs to persist through container restarts, you will also need to mount that volume to your host (ex: -v ./proget-logs:/var/proget/logs).
Enabling With Load Balancing/High Availability
Windows
To enable HTTP Request Logging in a Windows cluster, you will need to edit the product configuration file directly on each node in the cluster. You will then need to add the EnableRequestLogging="true" and the RequestLoggingDirectory="C:\ProgramData\ProGet\Logs" attributes to the WebServer node.
Example ProGet.config file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<InedoAppConfig>
<PostgresConnectionString Enabled="true">Host=127.0.0.1;Database=buildmaster;Username=proget;Password=*************</PostgresConnectionString>
<EncryptionKey>******************************************</EncryptionKey>
<WebServer Enabled="true" Urls="http://*:8624" EnableRequestLogging="true" RequestLoggingDirectory="C:\ProgramData\ProGet\Logs" />
</InedoAppConfig>
Docker
Enabling HTTP Request Logging in a Docker cluster requires you to enable request logging on each container in the cluster.
Log File Management
Log files will grow to a maximum size of 5MB and ProGet will retain up to 60 log files. When the maximum size is reached, ProGet will create a new log file and delete the oldest log file if there are more than 60 log files.
Log File Format
The log files are stored in the W3C Extended Log File Format, which is a standard format for logging HTTP requests. Each log file contains a header section that describes the fields in the log file, followed by a series of log entries, one per line. Each log entry contains the following fields. If a value is not available, a hyphen (-) will be used.
- date: The date when the request was received.
- time: The time when the request was received.
- c-ip: The IP address of the client making the request.
- cs-username: The username of the authenticated user making the request.
- s-computername: The name of the server handling the request.
- s-ip: The IP address of the server handling the request.
- s-port: The port number of the server handling the request.
- cs-method: The HTTP method used for the request (e.g., GET, POST).
- cs-uri-stem: The URI stem of the requested resource.
- cs-uri-query: The query string of the requested resource.
- sc-status: The HTTP status code returned to the client.
- time-taken: The time taken to process the request, in milliseconds.
- cs-version: The version of the HTTP protocol used for the request.
- cs-host: The host header sent by the client.
- cs(User-Agent): The user agent string sent by the client.
- cs(Referer): The referer header sent by the client.
- cs(x-client-ssl-protocol): The SSL protocol used by the client.
- cs(x-forwarded-for): The original IP address of the client, if the request was forwarded.
- cs(X-forwarded-host): The original host requested by the client, if the request was forwarded.
- cs(X-forwarded-port): The original port used by the client, if the request was forwarded.
- cs(X-forwarded-proto): The original protocol used by the client, if the request was forwarded.

