HOWTO: Publish Private PowerShell Modules
Storing your private PowerShell modules publicly on PowerShellGallery.com is not an option for most organizations.
ProGet allows you to set up a private repository. ProGet’s feeds allow you to securely store and share PowerShell modules with all members of your organization without the risks associated with a public repository.
This article explains how to create a PowerShell module repository in ProGet and then create, publish, and install private packages from it.
Step 1: Create a PowerShell Module Repository in ProGet
Create a new feed by navigating to "Feeds" > "Create New Feed"
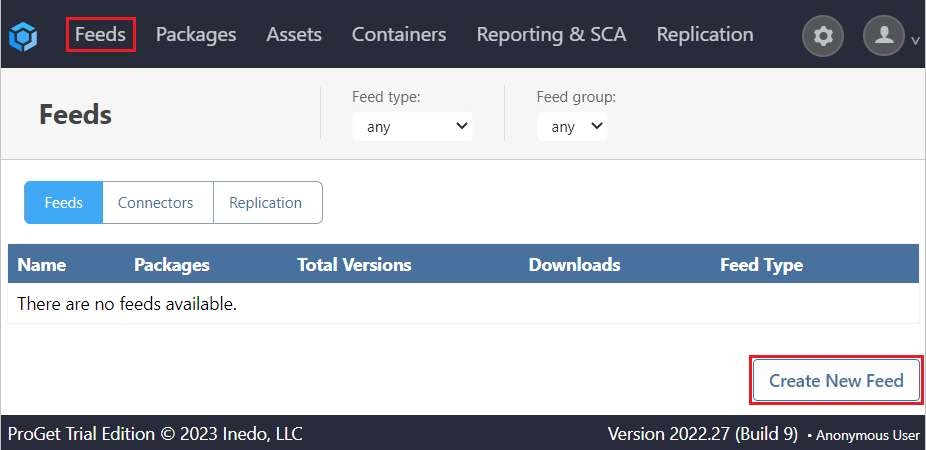
Choose "PowerShell Modules" from the options presented and give it a name and optional description. We’ll be using “internal-powershell”.
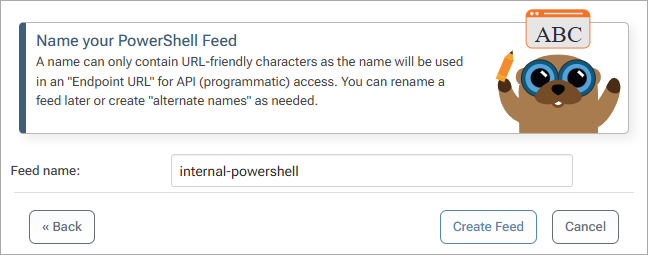
After clicking on "Create New Feed", you now have your own private PowerShell module repository!
Step 2: Create a PowerShell Module & Manifest
First, you will need to create a PowerShell Module. Modules combine several PowerShell functions into a single reusable and easily sharable resource.
For demonstration purposes, we’ll create a simple PowerShell Module named Foobar.psm1 and save it to C:\Foobar.
function Get-Foobar {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Take the inputs for two variables $Foo and $Bar. Then return $Foo$Bar
.PARAMETER Foo
Foo
.PARAMETER Bar
Bar
#>
param ([String]$Foo = "Foo", [String]$Bar = "Bar")
return "$Foo$Bar"
}
function Set-Foobar {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Take the inputs for two variables $Foo and $Bar. Then return $Foo$Bar
.PARAMETER Foo
Foo
.PARAMETER Bar
Bar
#>
param ([String]$Foo = "Foo", [String]$Bar = "Bar")
Write-Debug "$Foo$Bar"
}
Create a PowerShell Module Manifest
A module manifest is a PowerShell data file (.psd1) that, is simply an “about” file for your module that contains information about the module, including the version number, copyright, exported variables, etc.
Microsoft published a guide on writing PowerShell module manifests, but to sum it up: you can use the New-ModuleManifest CmdLet to create the manifest, and only the Author and Description metadata fields are required.
Using our Foobar.psm1 example we would type:
New-ModuleManifest -Path "C:\Foobar\Foobar.psd1" -Author Inedo -Description "Contains functions that will write Foobar to the console and debug" -PassThru
While building modules, consider how your team can adopt and leverage them. You can read more about making modules more effective across your organization on the Inedo blog.
Step 3: Publish Your Module to ProGet
Once you have a PowerShell module set up, you can add it to your ProGet feed to securely share it with your entire organization.
Create an API key in ProGet
You will need to create an API Key that allows your PowerShell module to connect to your ProGet instance. To do this navigate to "Administration Overview" > "Integrations & Extensibility" > "API Keys" > "Create API Key".
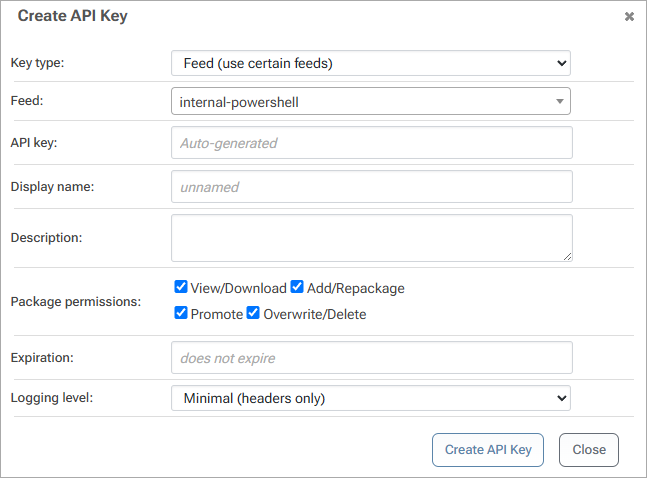
ProGet uses three types of API keys, but since we created a PowerShell feed in Step 1, we'll use a feed API key. If you need a temporary API key, you can specify the following as the API key instead:
username:password
For more information on how API Keys function in ProGet, see our documentation
Import PowerShellGet Module
PowerShellGet is a module that allows you to both publish to and import from a repository. It is installed by default, but running the command will ensure that the module is up to date.
To do this in PowerShell, enter:
Import-Module PowerShellGet
Register Target Feed
By default, PowerShell attempts to publish modules to and obtain them from the PowerShell Gallery, Microsoft's public PowerShell module repository. To publish a PowerShell module to ProGet, a new repository must be registered.
To do this, you'll first need to find the API Endpoint URL of your feed:
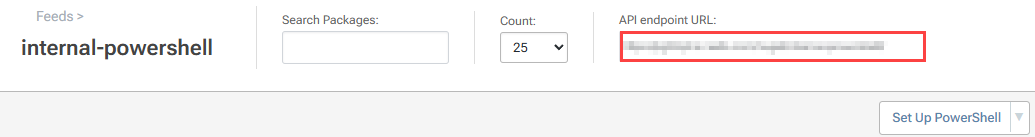
Then, you can use the cmdlet Register-PSRepository to designate a new target repository.
You’ll also need to use the following parameters to publish to your ProGet PowerShell repository/feed:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Name | Name of the feed you created |
| -SourceLocation | The API Endpoint URL |
| -PublishLocation | Also the API Endpoint URL |
Using our Foobar.psm1 example we would type:
Register-PSRepository -Name internal-powershell -SourceLocation http://54.250.56.60:8624/nuget/internal-powershell/ -PublishLocation http://54.250.56.60:8624/nuget/internal-powershell/
Publish Module to ProGet Feed
To publish the module, use the cmdlet Publish-Module in combination with the following parameters:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Path | The location of the target module on your system |
| -NuGetApiKey | The API key you are using to connect your PowerShell to ProGet |
| -Repository | The repository you registered earlier (i.e. name of the feed) |
| -verbose | Optional, but displays additional information that can help you identify errors if any occur |
Using our Foobar.psm1 example we would type:
Publish-Module -Path c:\Foobar -NuGetApiKey http://54.250.56.60:8624/nuget/internal-powershell/ -Repository internal-powershell -verbose
At this point "Foobar" will now appear in your ProGet feed.
Step 4: Install Modules from your ProGet Feed
To use a PowerShell module in your ProGet feed, you must first download and install the module on the target system.
Open PowerShell and register the feed from which you want to download the module. As with publishing, it is necessary to specify a custom location instead of the default PowerShell gallery.
Register ProGet Feed for Downloads
Use Register-PSRepository in combination with the following parameters:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Name | The name of the feed you want to download the module from |
| -SourceLocation | The location path of the feed |
ProGet will display the command to use under Usage Instruction in: Feeds > feed-name > module-name > Repository.
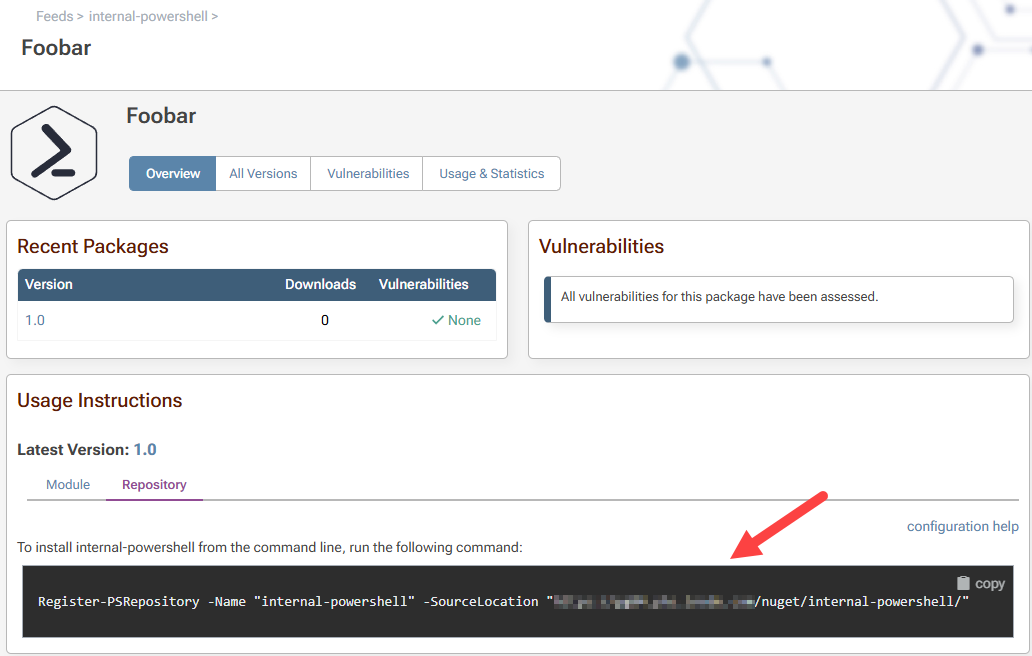
Using our “Foobar.psm1” example we would type:
Register-PSRepository -Name "internal-powershell" -SourceLocation "http://54.250.56.60:8624/nuget/internal-powershell/"
If you get an error message saying that “«feed-name» exists,” run the following code and try registering the new feed again:
Unregister-PackageSource -Name «feed-name»
Download and Install Modules from Your ProGet Feed
Use Install-Module with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -Name | Name of the module you want to download |
| -RequiredVersion | Version of the module you want to download as specified in the module manifest. Note that ProGet will keep a copy of the versions of your module as you update it |
| -Repository | Name of the feed you are downloading the module from |
ProGet will display the command to use under Usage Instruction in: Feeds > feed-name > module-name > Repository.
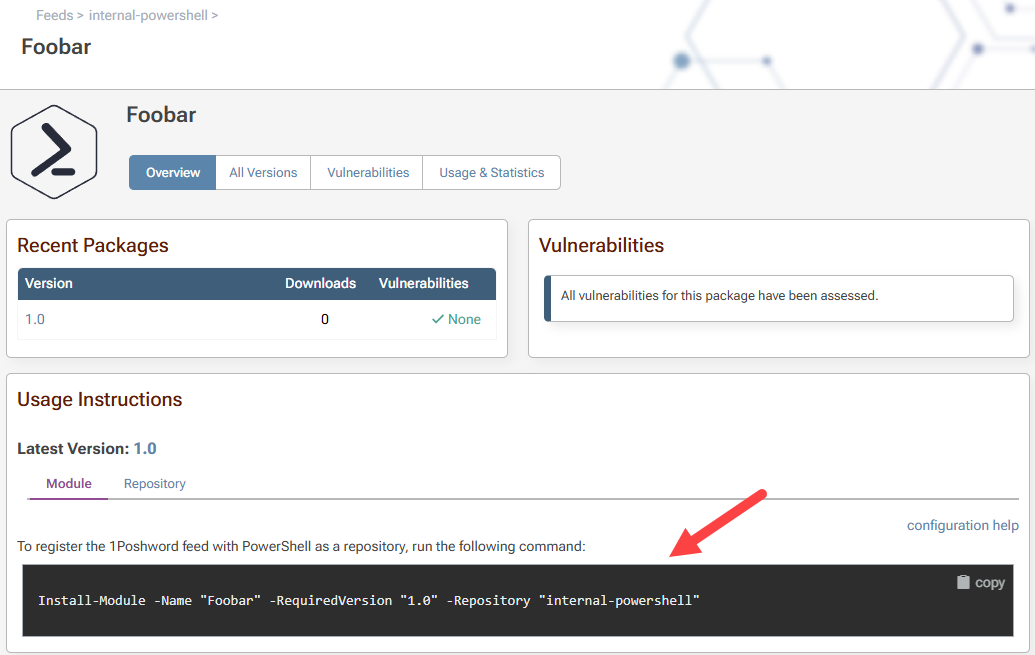
Using our “Foobar.psm1” example we would type:
Install-Module -Name "Foobar" -RequiredVersion "1.0" -Repository "internal-powershell"

