HOWTO: Proxy Recipes from Conan Center in ProGet
ProGet lets you create "Feeds" to proxy Conan recipes from Conan Center. This feed can then be configured as a remote locally, allowing you to install Conan recipes/packages as you would when installing them directly from Conan Center.
Using ProGet as a proxy will let you assess vulnerabilities in Conan packages, provide statistics on which packages are being downloaded and used frequently, and also cache packages to ProGet, allowing your team to access and install them even if Conan Center is experiencing network issues.
This page will explain how to set up a Conan feed in ProGet to proxy packages. It will also cover how to create a private repository for your internal Conan packages.
Step 1: Create a New Feed
First, you will need to create a Conan feed that will proxy Conan packages from Conan Center. Select "Feeds" and "Create New Feed". Next, select "Conan Packages" under "Developer Libraries".
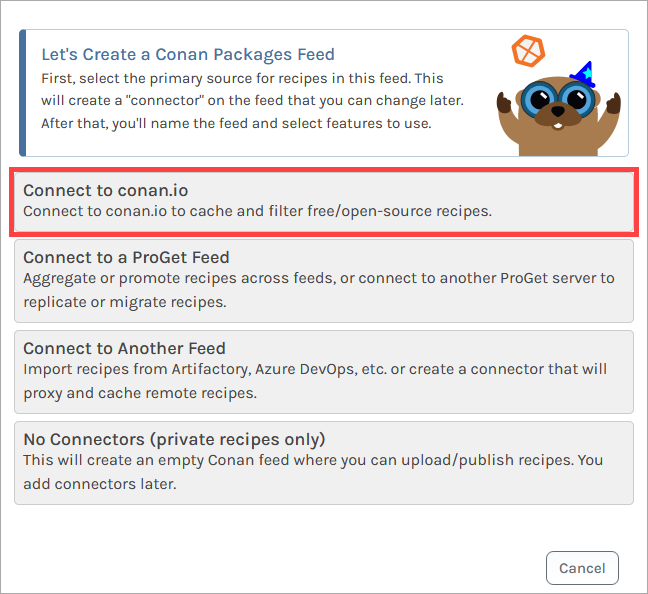
Now select "Connect to conan.io" which will allow us to proxy packages from Conan Center.
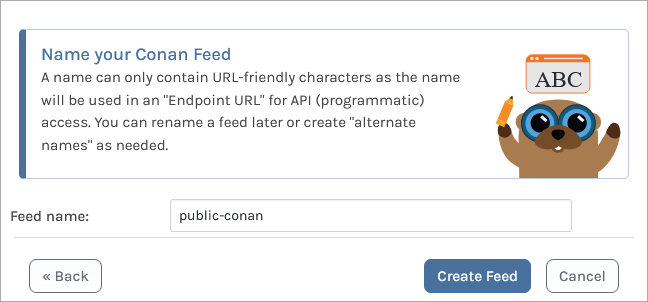
Then select "No, Create One Feed", as we will be creating a single feed to proxy Conan packages. From here, name the feed (in this example, we've called it public-conan). Then click "Create Feed".
You'll then be given options to configure ProGet's Vulnerability Scanning and Blocking and Licensing Detection and Blocking features, letting you assess vulnerabilities and create policies for licenses. Select "Set Feed Features", which will create the feed, and redirect you to the newly created public-conan feed.
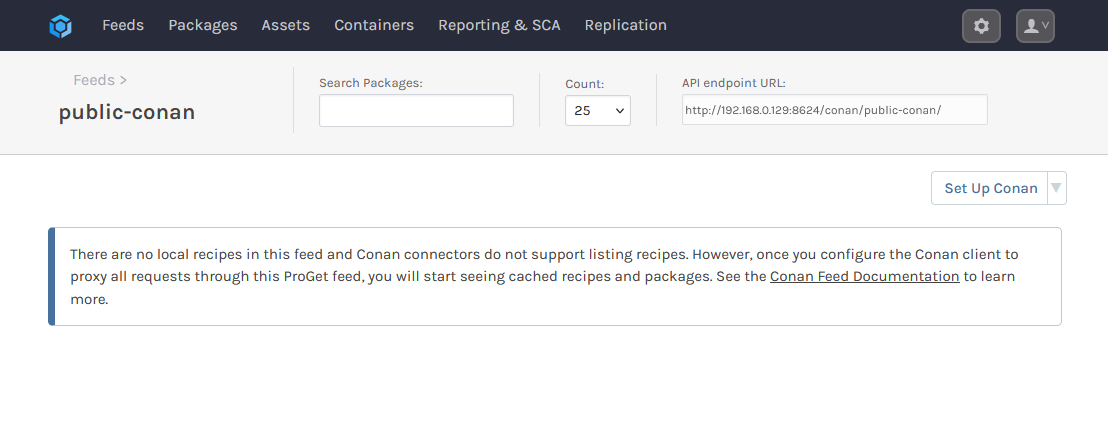
ProGet feeds configured with a connector will normally list packages proxied from an external source. However, Conan connectors do not support listing proxied recipes. Once you configure your Conan client to proxy all requests through this ProGet feed, you will start seeing cached recipes and packages.
Step 2: Configure the Feed as a Remote
To let your teams use the public-conan feed when installing packages from their Conan V2 client, you will need to add it as a remote using the conan remote add command.
$ conan remote add public-conan https://proget.corp.local/conan/public-conan/
If you are using a self-signed certificate with ProGet, you will also need to add the --insecure argument:
$ conan remote add public-conan https://proget.corp.local/conan/public-conan/ --insecure
Recommended: Removing Conan Center as a Remote
Even after adding your public-conan feed as a remote, the Conan client will still use Conan Center unless you explicitly disable it. This would allow developers to still install packages directly from Conan Center. We recommend disabling Conan Center to make sure all requests are proxied through your ProGet feed.
$ conan remote disable conancenter
Step 3: Installing Conan Packages
Before installing packages you will need to configure a build profile. You can create a default profile with the conan profile detect command or specify your own profile with --profile:build=«myprofile»
To install Conan packages from your public-conan feed, use the install command:
$ conan install --requires=mypackage/1.2.3 -r=public-conan
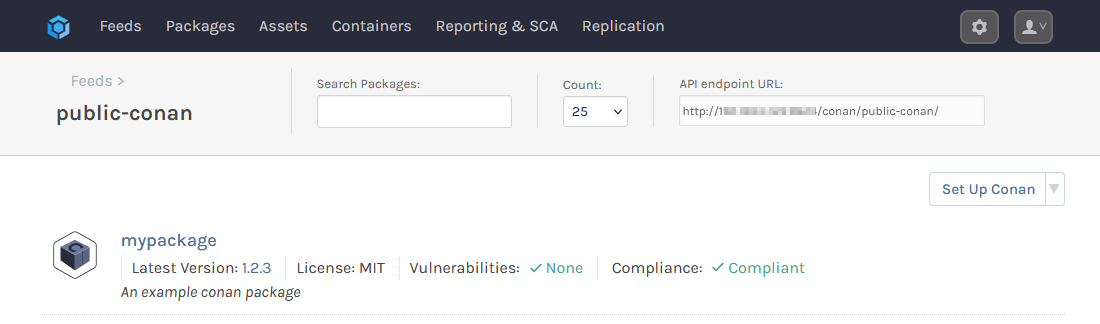
Cached Packages in ProGet
Once you have installed a package by proxying through your public-conan feed, it will be cached in ProGet, and can be viewed in the feed
(Optional) Authenticating to Your Conan Feed
By default your public-conan feed does require authentication, and packages can be proxied and installed anonymously. However if your Conan feed is configured to require authentication, you can follow these steps to authenticate to it.
You can use a username/password to authenticate to a Conan feed, however we strongly recommend Creating a ProGet API Key to authenticate, using api as the username and your key as the password.
(Optional) Creating a Package Approval Flow
In this guide we looked at proxying packages from Conan Center. However, without appropriate oversight, developers will be able to install any OSS packages from the repository, which may risk introducing vulnerabilities or packages with unwanted licenses. We recommend implementing some form of vetting of the packages used in your development, which can be achieved by creating a "Package Approval Flow".
To set up a package approval flow, refer to HOWTO: Approve and Promote Open-source Packages. The guide uses NuGet feeds as an example, but the steps are identical when creating Conan package feeds.
After creating your "Unapproved" and "Approved" feeds, follow the steps in "Add the Feed as a Remote to Your Conan Client" to add the "Approved" feed (e.g. conan-approved) as a remote.

