HOWTO: Use Approved PowerShell Gallery Packages (Optionally Offline)
By using ProGet, teams can restrict access to Microsoft’s public PowerShell module repository, the PowerShell Gallery, ensuring that only approved packages are ever used.
By default, PowerShell attempts to pull and publish from powershellgallery.com. That’s not great for teams that work offline or teams that need a package approval workflow in place.
This article will run through a standard example scenario of a company, Kramerica, configuring ProGet to create a package approval workflow to ensure only approved packages from the PowerShell Gallery are available for all the operation team to use. This configuration would also allow the feed to be used offline.
Step 1: Create an Unapproved Package Feed.
In this guide we'll need to create two "PowerShell" feeds, one for unapproved packages, and the other for approved packages that have been promoted. We'll start by creating the "unapproved" feed to proxy open source packages from PowerShell Gallery. Start by selecting "Feeds" and "Create New Feed".
Next, we need to select "PowerShell Modules" as we will be using packages from "PowerShell Gallery".
After selecting the feed type, select "Free/Open Source PowerShell Modules" to connect directly to PowerShell Gallery.
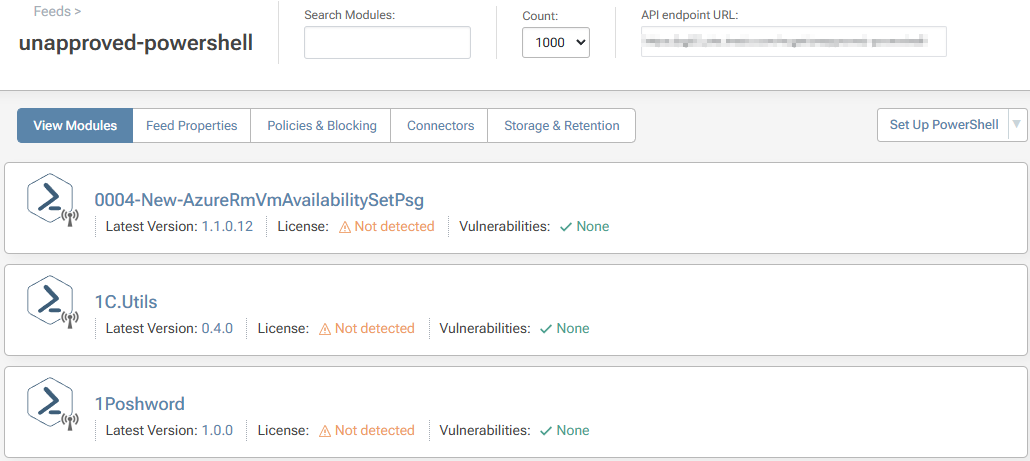
From here, name the feed. In this case we'll call it unapproved-powershell.
Select "Create New Feed" to be redirected to your empty unapproved-powershell feed, now populated with packages from PowerShell Gallery.
Step 2: Create an Approved Package Feed
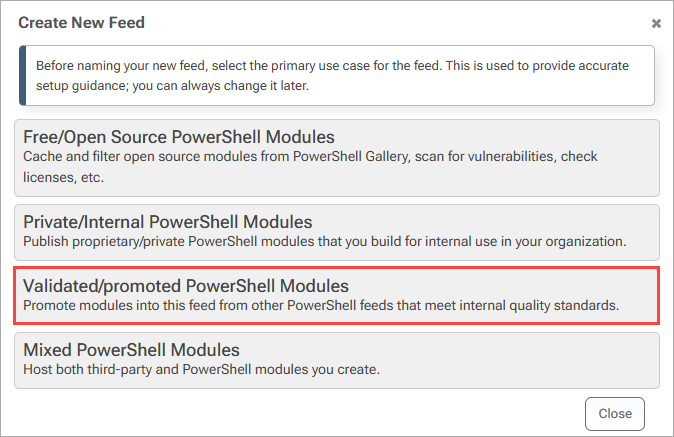
Next, we'll create a feed to promote package that have been assessed and approved. Once again, select "Feeds", "Create New Feed", and "PowerShell Modules". Now you will be able to select "Validated/promoted PowerShell Modules".
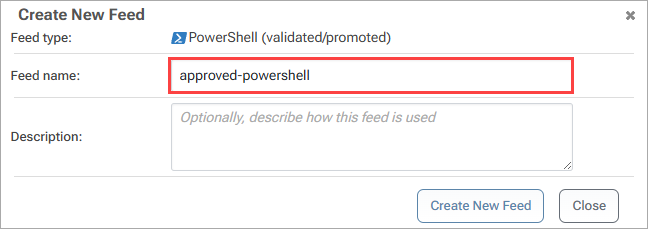
Once again, name the feed. Here, we'll call it approved-powershell.
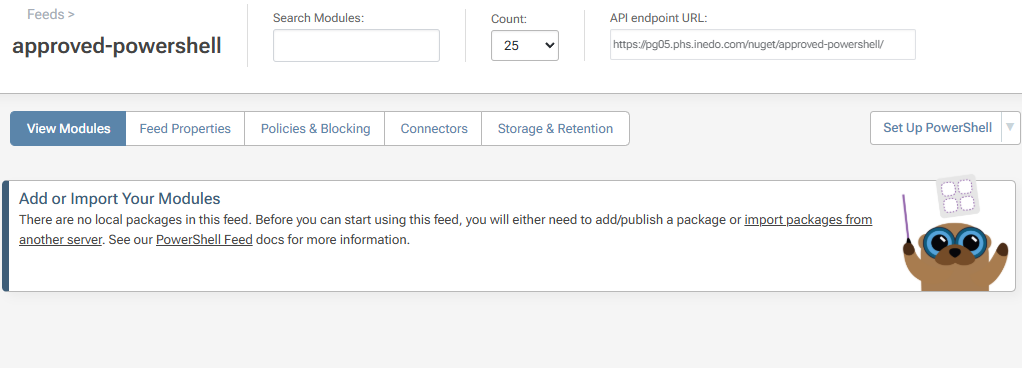
Select "Create New Feed" to be redirected to your empty approved-powershell feed.
Step 3: Promoting Packages
Now both your unapproved and approved PowerShell feeds are created, you can promote verified modules to your approved feed.
First, locate the module and version you wish to promote in your unapproved-powershell feed. On the module overview page access the drop-down menu, and select "Promote Package".
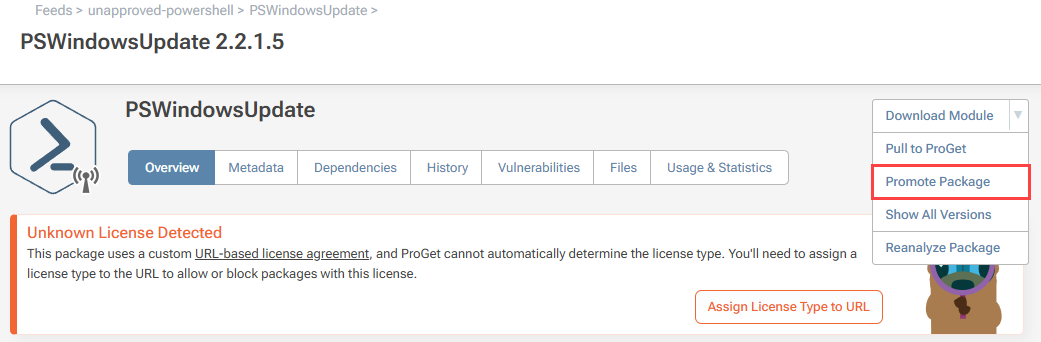
You will then be presented with your existing PowerShell feeds and can choose which one to promote the module to. You can also add a comment to provide a reason for promoting the module.
In this case, we'll choose our approved-powershell feed, and select "promote".
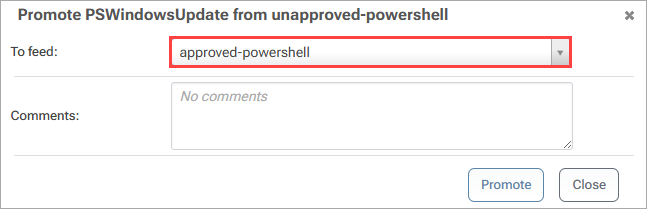
Navigating to our approved-powershell feed, we can see that the module has been successfully promoted to the feed.
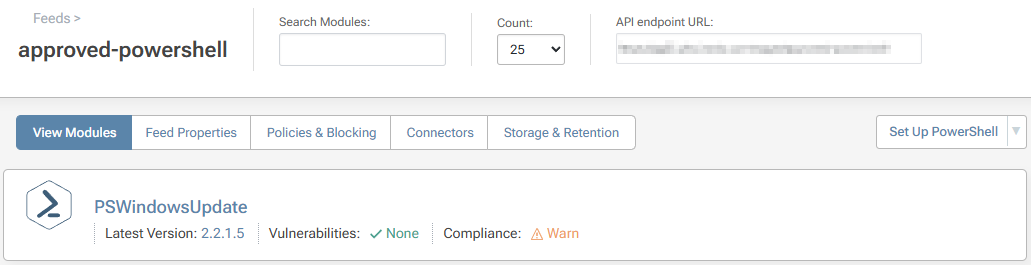
Optional: Configure 'approved-powershell` as the Promotion Target
An alternative option is to configure approved-powershell as specific target to promote to. This way, modules from the unapproved-powershell feed can only be promoted to a singular approved feed that you have specified.
To do this, navigate to the "Feed Properties" tab in unapproved-powershell. In the "Other settings" menu navigate to "Promote To Feed" and select "change".
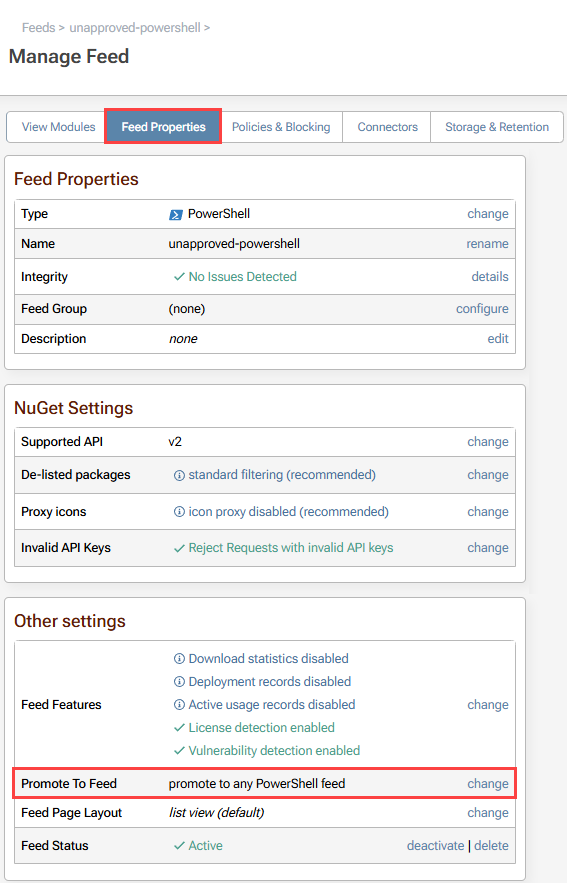
Choose your approved-powershell feed from the drop-down menu and select "Save".
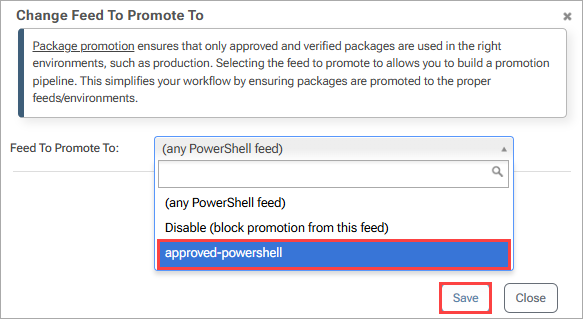
Now when promoting packages from your unapproved-powershell feed, you'll only have the option to promote to the specified approved feed.
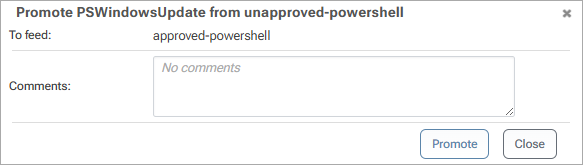
Step 3: Set Permissions
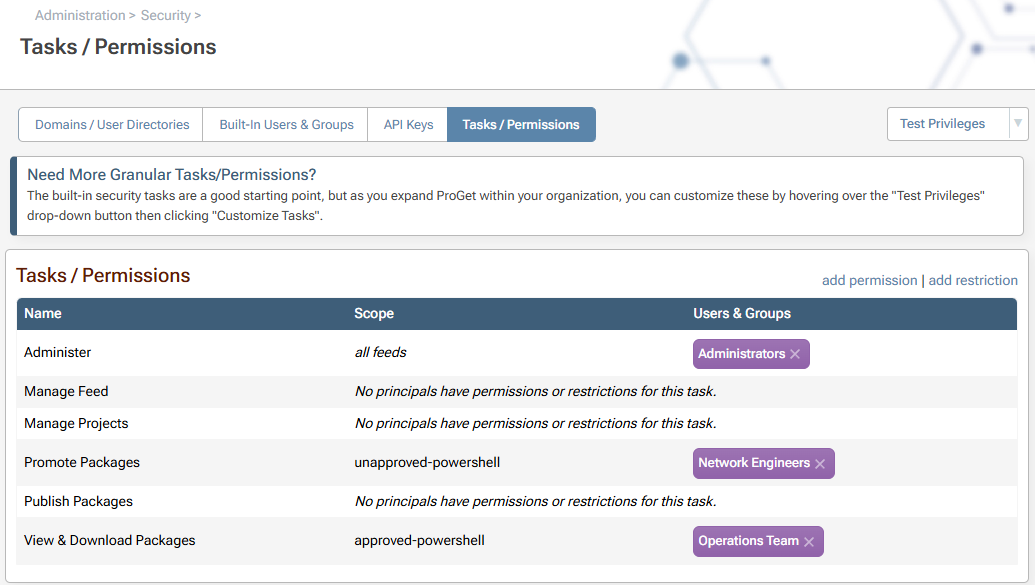
There are many ways to configure security access controls for uses and groups in ProGet. In this example, we want to permit only network engineers to promote packages in the approved-powershell feed, since they're trained to check the quality, licenses, and vulnerabilities of open-source packages. To ensure this rule, we'll set up a new permission. By default, only administrators have assigned permissions.
To start, we navigate to "Settings"> "Manage Security".
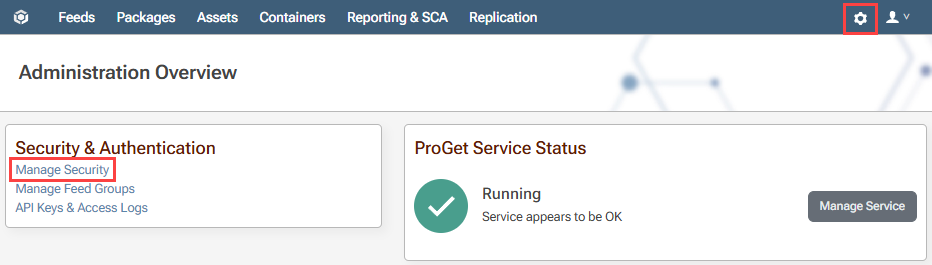
We then navigate to the "Tasks / Permissions" tab, listing the currently configured permissions, and select "add permission".
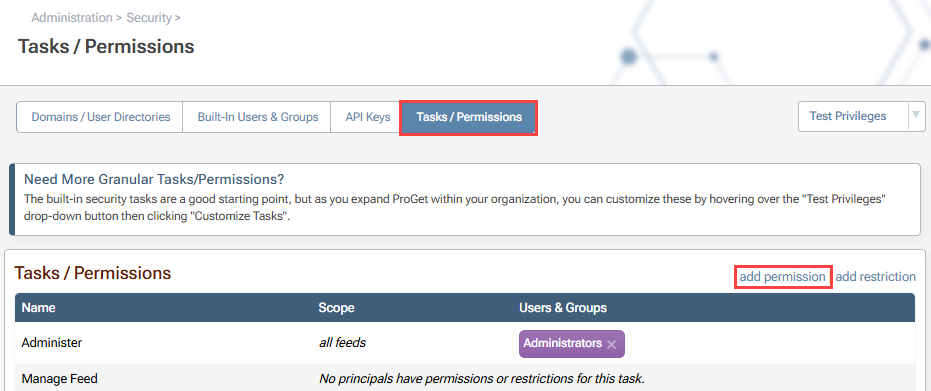
Next, we will fill out the following dialog to give the "Network Engineers" user group permission to "Promote Packages" from the unapproved-powershell feed.
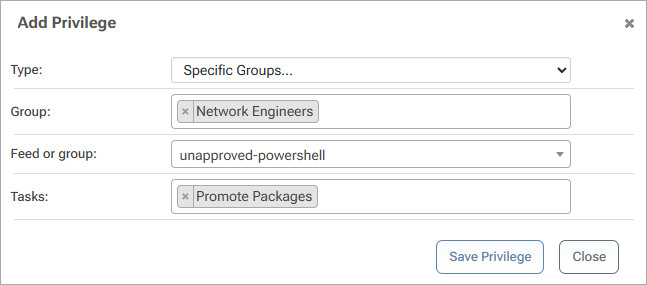
Following the same steps, we will also give the "Operations Team" user group permission to "View and Download" packages from the approved-powershell feed.
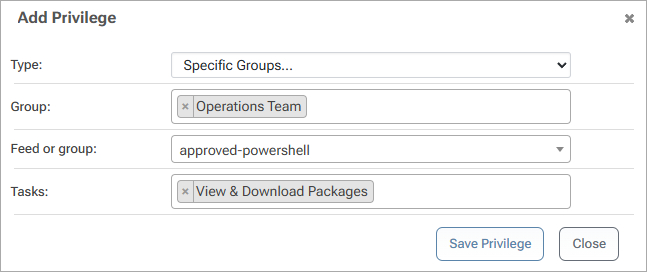
After saving these two privileges, the task overview page looks like this:
Step 4: Configure Your Feeds with PowerShell
To use this newly created feed with PowerShell, we first need to find the endpoint URL on the Feed Overview page and register it as a source.
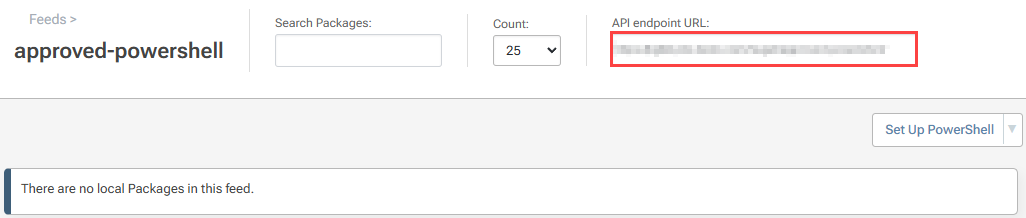
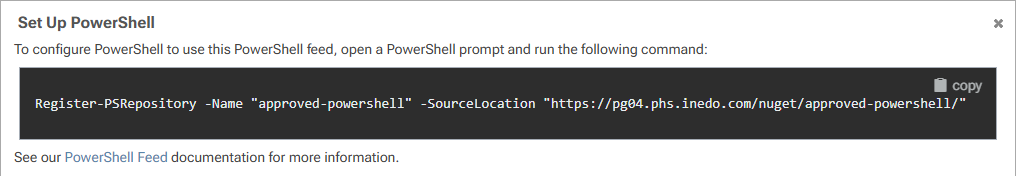
To register this endpoint, we'll use the Register-PSRepository cmdlet with the following parameters:
-Name- the name of the approved packages feed-SourceLocation- the Endpoint URL of the approved packages feed
We can find the required line already set for us by selecting "Set Up PowerShell" on the right-hand side, which will bring up a dialog we can copy from:
However, PowerShell will try to pull modules from the PowerShell Gallery, so we need to unregister it using the Unregister-PSRepository cmdlet. That only requires one parameter (Name), which is PSGallery by default.
Register-PSRepository -Name approved-powershell -SourceLocation https://«host-name»/nuget/approved-powershell
Unregister-PSRepository -Name PSGallery
After that, PowerShell will only use the approved packages feed for modules, without needing to access the public PowerShell Gallery.
Note that, if we want to publish packages to this feed, we'll need to also specify the PublishLocation parameter as well. This would be the same as SourceLocation.

