GitLab
GitLab is a DevOps platform that has support for source control hosting, issue tracking, collaboration tools, and cloud-native deployment. While GitLab has support for its own pipelines, BuildMaster is designed to work alongside GitLab to provide a self-managed CI/CD solution using BuildMaster's Git Integration and Issue Tracking.
Connecting to GitLab
BuildMaster's Git Integration allows you to connect to GitLab at application creation or through the application's settings page. To connect BuildMaster to GitLab:
- Either create a new application or add a new connection on the application settings page, then select Git Repository
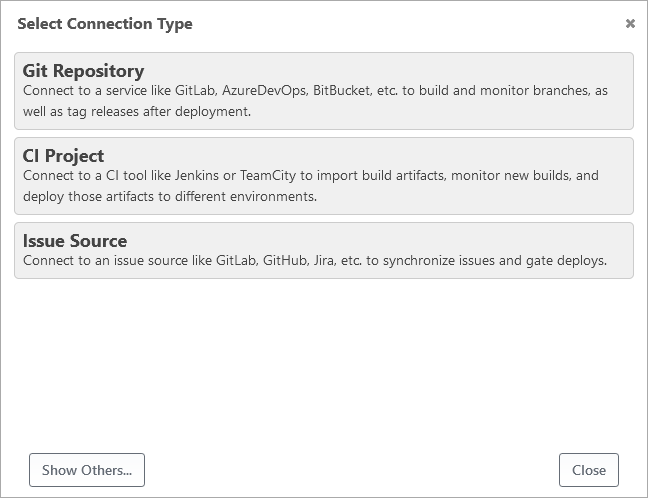
- Select the GitLab connection type
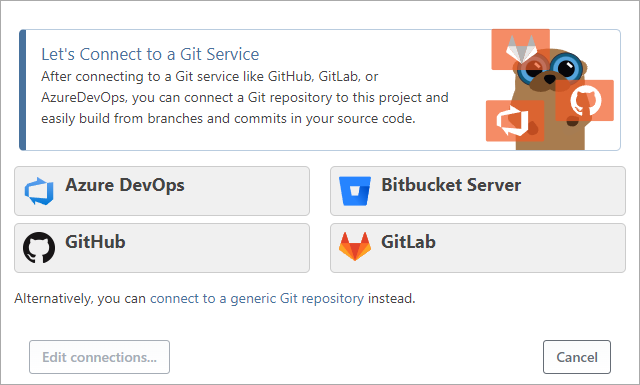
- Enter your GitLab user name and personal access token and click Select GitLab Repository
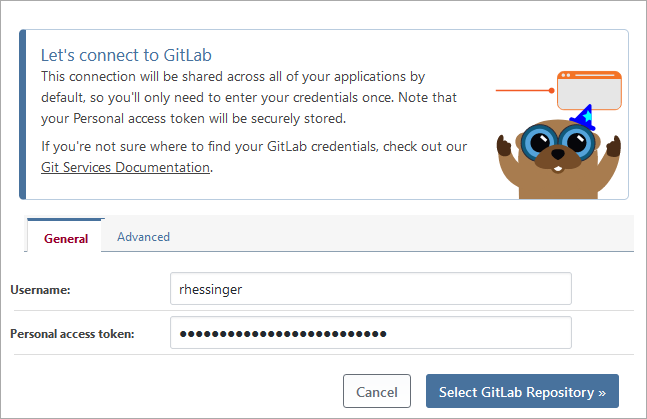
- Select your GitLab namespace and enter or select your repository and click Save Repository
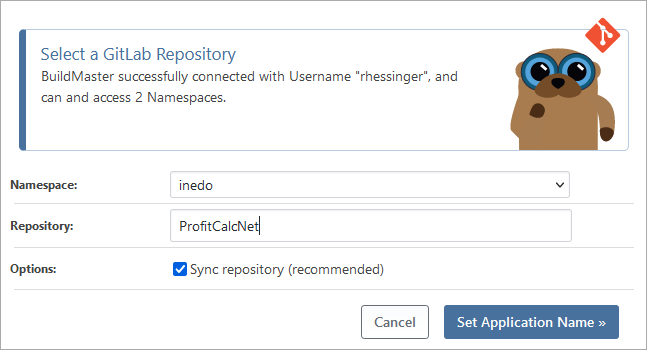
The GitLab repository will then be synchronized to your server and you will see a successfully synced message.
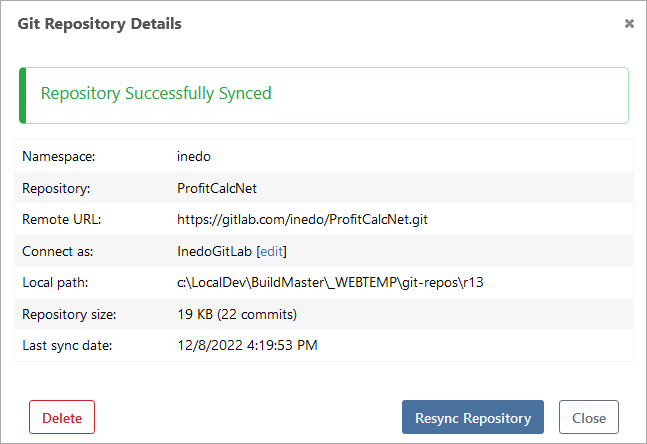
Editing a GitLab Connection
You can edit these items directly to enable advanced scenarios (such as a shared repository) by clicking view all on the Settings page, or by going to Admin > Credentials & Resources. See Credentials & Resources to learn more.
Generating a GitLab Personal Access Token
When connection BuildMaster to GitLab, you need to use a GitLab Personal Access Token (PAT). To generate this token:
- Navigate to your GitLab project
- In the upper right corner, click your user icon, and then click Preferences
- Navigate to Access Tokens
- Enter a token name, expiration, and select the following scopes
- read_api
- write_repository
- Click Create personal access token
Browsing GitLab Repositories
After adding a synchronized GitLab repository to an application, you can browse the branches, source code, and commits of that repository, as well as the changes between builds/releases, directly on the web from BuildMaster UI. See our synchronized git repositories documentation to learn more.
When viewing branch, tag, or commit details, you can also click the Browse in GitLab link to view the details directly in GitLab.
Issue Tracking
When you connect your BuildMaster application to a GitLab issue tracker, your issues are automatically synchronized with BuildMaster's issues. This allows you to browse issues, associate them with specific releases, and block releases if there are untested or unresolved issues in BuildMaster.
BuildMaster also allows you to create or update your Issues with OtterScript operations.
GitLab and Scripting
When your application uses a synchronized GitLab repository, you'll be able to create a build from any commit in the repository. When creating a build in this manner, the selected commit - along with its branch and repository - will be associated with that build and displayed throughout the UI. You can access those values in scripts with the $Commit, $Branch, and $Repository variable functions. See Git Build Scripts & Automations for more information.
GitLab Git Operations
The GitLab integration supports all the standard BuildMaster Git operations, but there are a couple things to keep in mind when using these operations.
Using Other Git Repositories
By default, Git::Checkout-Code will use your Git Connection to connect to your repository. If you would like to select a repository that is different than what your Git connection specifies; navigate to your repository in GitLab, click the "Clone" button and copy the URL under Clone with HTTPS, then set the RepositoryUrl parameter to it in theGit::Checkout-Code operation.
In cases like this, you can specify input parameters like this.
Git::Checkout-Code
(
RepositoryUrl: https://gitlab.com/inedo/ProfitCalcNet,
BranchOrCommit: master,
To: c:\build\space\src,
CommitHash => $CommitId
);
Log-Information Checked out at $CommitId from my-repo;
Git::Set-CommitStatus Operation
GitLab allows you to set the "status" of a particular commit, as it relates to a successful build. This status is often displayed in GitLab's UI when listing commits.
To set this status in BuildMaster, you can simply call the operation with the desired status. In general, you'll want to use a try..catch statement as follows:
Git::Checkout-Code;
Git::Set-CommitStatus pending;
try
{
... perform build operations...
Git::Set-CommitStatus success;
}
catch
{
Git::Set-CommitStatus error;
throw;
}
Like the Git::Checkout-Code operation, the operation will use $Commit and $Repository if you don't specify them as parameters. The operation can also automatically determine the status, but you can override that by specifying the Status parameter:
pending- a build is about to start or is runningrunning- a build is currently runningsuccess- build completed successfullyfailed- execution didn't complete or there was an error unrelated to build compilation/testscanceled- an execution was canceled
GitCreate-PullRequest and GitMerge-PullRequest
Just like Git::Checkout-Code, the Git::Create-PullRequest operation will use your Git Repository connection to create a merge request in GitLab. Here is an example of using a repository that is different than what your Git Repository connection specifies:
Git::Create-PullRequest
(
Title: My New Thing,
Target: main,
Repository: https://gitlab.com/inedo/ProfitCalcNet
);
This operation will also record the ID of the Pull Request on the Build, so that you can later access it with $PullRequestId.
The Feature Branch Workflow Pipeline will create a script with the Git::Create-PullRequest operation. Try it out to see this in action.
You may want to extend your Feature Branch workflow and let BuildMaster do the merging.
To complete a merge request, you can run the operation without parameters:
Git::Merge-PullRequest;
This will use the $PullRequestId if you don't specify it as a parameter.
GitLab Issue Operations
Although BuildMaster has an issue source to synchronize issues between BuildMaster and GitLab, there are times where you need to work with these issues and milestones in your build and release scripts. The following operations are supported in BuildMaster and will use the credentials, API URL, namespace, and project specified in your GitLab resource. You can also override these values with the following parameters:
- UserName
- Password
- Namespace
- Project
- ApiUrl
GitLab::Create-Issue
This operation allows you to create a new issue in GitLab.
To add a new work item in the Kramerica project under the 1.1.0 milestone, you can use this operation:
GitLab::Create-Issue
(
From: GitLabCredentials,
Title: QA Testing Required for $ApplicationName,
Description: This issue was created by BuildMaster on $Date,
Milestone: 1.1.0,
IssueId => $IssueId
);
This example will allow you to update/close the issue in other operations by using the $IssueId variable.
You can also specify a list of tags (ex: Labels: @(Label1, label2)), a list of assignees (ex: Assignees: @(sdennis)), or other additional properties (ex: AdditionalProperties: %(weight: 1000, confidential: true)) when creating the issue.
GitLab::Create-IssueNote
This operation allows you to add a note to a GitLab issue.
To add a note to an issue, you can use this operation:
GitLab::Create-IssueNote
(
Credentials: GitLabCredentials,
IssueId: $IssueId,
Body: Issue was fixed in version $ReleaseNumber
);
GitLab::Close-Issue
This operation allows you to close a GitLab issue.
To close an issue, you can use this operation:
GitLab::Close-Issue
(
Credentials: GitLabCredentials,
IssueId: $IssueId
);
GitLab::Ensure-Milestone
This operation ensures a milestone exists at the specified status.
To create a milestone, you can use this operation:
GitLab::Ensure-Milestone
(
Credentials: GitLabCredentials,
Title: $ReleaseNumber,
StartDate: $Date,
DueDate: $Date,
Description: Automated release for $ReleaseNumber,
State: open
);
To close a milestone theat already exists, you can use this operation:
GitLab::Ensure-Milestone
(
Credentials: GitLabCredentials,
Title: $ReleaseNumber,
State: closed
);
Installing the GitLab Extension
The GitLab extension is installed by default when you install BuildMaster. You can update the extension by simply navigating to the Admin > Extensions page in your BuildMaster instance and clicking the update link to the right of the GitLab extension. Once the GitLab extension has been updated, it can be reverted back to the built-in version by navigating to Admin > Extensions > GitLab and then selecting the Change Version button in the upper right corner.
If your instance doesn't have Internet access, you can upgrade/downgrade it by manually installing the GitLab extension after downloading the GitLab Extension Package.
Built-in extensions cannot be deleted or downgraded past the included version.

