HOWTO: Publish RPM Packages to a Private Repository in ProGet
Using ProGet, you can easily set up a private repository to publish and store your internal RPM packages.
This guide will show you how to set up a "Feed" in ProGet to as a private RPM package repository. We will also walk you through creating your own packages and publishing them to this feed.
Step 1: Create a New Feed
Start by creating an RPM feed to host your packages. Select "Feeds" and "Create New Feed". Next, select "RPM Packages".
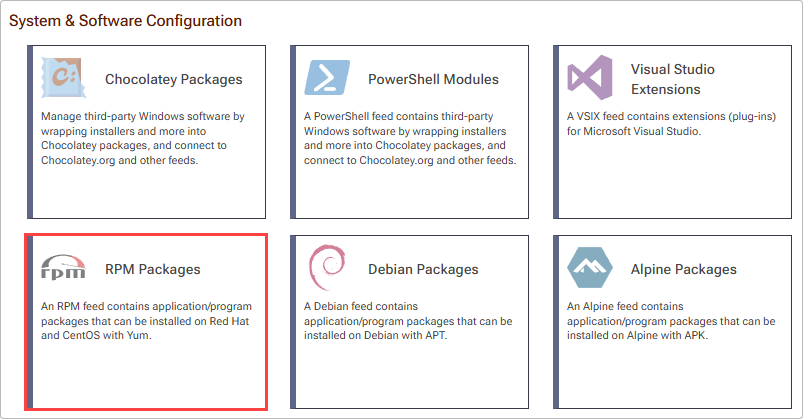
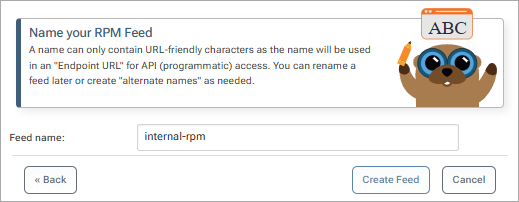
Now name your feed. For this guide, we will call it internal-rpm. Then select "Create Feed".
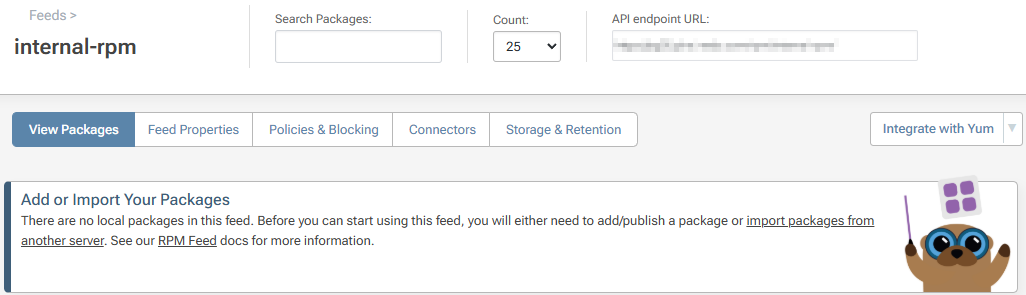
You will then be redirected to your new internal-rpm feed, currently empty.
Step 2: Create an API Key
Now create an API Key which will allow your local RPM environment to authenticate to the internal-rpm feed to publish packages to it, as well as install them once published.
You can read more about creating API keys in ProGet on our API Key page.
When creating an API Key, fill in the fields by selecting "Feeds (Use Certain Feeds)" as the "Feed Type" and selecting the internal-rpm feed. Then set the API key. You can use any alphanumeric sequence, or just leave it blank to autogenerate one.
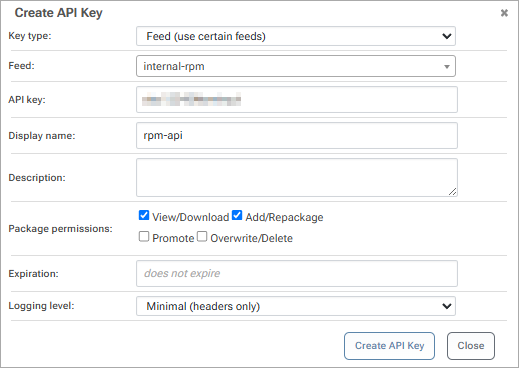
Make sure the "View/Download" and "Add/Repackage" boxes are checked, and then select "Save".
Step 3: Build Your Package
Next, we will build and publish our packages. You can follow the official Red Hat documentation to learn more about creating packages. To build your package you will need to install rpmdevtools if you haven't already by entering:
$ sudo dnf install rpm-build rpmdevtools
And then set up the build environment by entering:
$ rpmdev-setuptree
Once you have the tarball (.tar.gz) and .spec file needed for the build, run the build command by entering:
$ rpmbuild -ba ~/rpmbuild/SPECS/«spec-file».spec
When the build is finished, the .rpm file will be located in the rpmbuild/RPMS folder, for example:
~/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/my-package-1.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
Step 4: Publish Your Package to ProGet
To publish your package to your ProGet RPM feed, you can use pgutil. This will require some minor configuration before use. This includes setting up your ProGet instance and API key as a source by running:
$ pgutil sources add --name=Default --url=«proget-url» --api-key=«api-key»
For example, adding the ProGet instance https://proget.corp.local/ with the API Key abc12345 you would enter:
$ pgutil sources add --name=Default --url=https://proget.corp.local/ --api-key=abc12345
Now upload your packages by entering:
$ pgutil packages upload --feed=«feed-name» --input-file=«path-to-package»
For example, uploading the package my-package-1.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm stored at /home/user/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/my-package-1.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm to your internal-rpm feed you would enter:
$ pgutil packages upload --feed=internal-rpm --input-file=/home/user/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/my-package-1.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
Your package will then be uploaded to the internal-rpm feed.
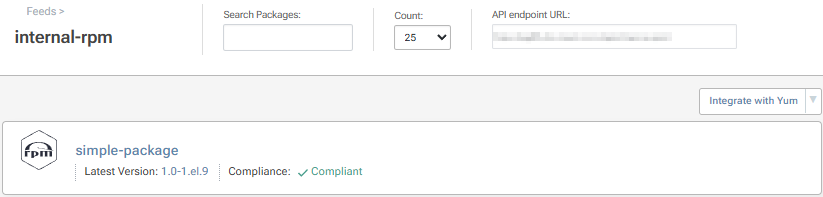
ProGet 2023 and Earlier
To push an RPM package via HTTP, issue a PUT or POST request with the package file as the content to: http://«proget-url»/rpm/feed-name»/
For example, to upload the RPM package mypackage-1.0.0.rpm to the feed internal-rpm with the API key abc12345:
$ curl http://proget.corp.local/rpm/internal-rpm/ --user api:abc12345 --upload-file mypackage-1.0.0.rpm
Step 5: Add the Feed to Your Local RPM Environment
To install packages from the internal-rpm feed, you'll need to add it as a source in the local RPM environment. For this, you will need feed's URL. This can be found at the top right of the feed's page.
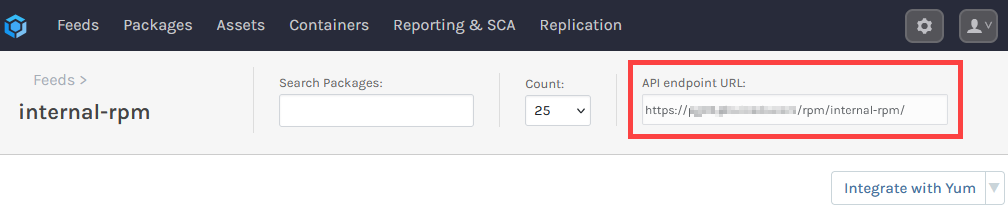
To add the feed, you'll need to create a .repo file locally. Create the file by entering:
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/internal-rpm.repo
In this case we used the vi text editor, but you can use any other such as nano. With the .repo file open, enter the following:
[internal-rpm]
name=InternalRpm
baseurl=http://proget.corp.local/rpm/internal-rpm/ # your RPM feed URL
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Then save and exit (:wq in the case of vi). You can confirm the feed has been set by listing the configured repositories:
$ yum repolist all
Or listing packages by entering:
$ yum list available --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo=internal-rpm
By default, repositories will already be configured, depending on the distribution of your local environment. We recommend removing these to install packages exclusively from your internal-rpm feed. You can remove a repository by entering:
$ sudo rm /etc/yum.repos.d/«repo-name».repo

