HOWTO: Filter Packages by License
ProGet makes it easy to allow, block, and filter open-source licenses, ensuring compliance and mitigating legal risks in your software development projects.
Nearly all open-source packages that you'll find on NuGet.org, npmjs.org, etc. have a license agreement that will legally bind the company to the package author's terms. Some licenses (like GPL-3) are not appropriate for closed-source software, and can put the company at serious legal risk. See How to avoid Costly Lawsuits from Unexpected Licenses to learn more.
In this article we will look at controlling open-source license usage in ProGet, and how you can block or allow licenses depending on your situational needs.
Controlling Open-Source Package License Use
You can take two different approaches in ProGet when controlling how you allow, block and filter the open-source licenses of your development project.
Blocking Unwanted Licenses (Blacklisting)
Often referred to as "Blacklisting", this will allow downloads of all packages except the ones with licenses you explicitly Prohibit". This is regarded as effective when targeting and blocking specific licenses, especially those known to have a history of causing legal or compliance issues.
It's also simpler and easier to manage, allowing you to progressively update the list as you encounter and become more aware of existing or new licenses that need to be restricted.
Allowing Only Specific Licenses (Whitelisting)
In contrast, often referred to as "Whitelisting", this will prohibit downloads of all packages except the ones with licenses you explicitly allow. This is far more efficient when your organization has very strict licensing policies and wants to ensure air-tight compliance in your production.
It also encourages greater control over your production environment as you define what is used, avoiding the risk of developers using unapproved licenses.
This guide will walk you through applying each approach in ProGet.
How to Block Unwanted Licenses (Blacklisting)
In this scenario, we want to take a list of licenses and decide on licenses we want to block, prohibiting downloading and production use. We'll start with "GPL 3.0" due to it's legal risks.
Step 1: Navigate to License
Navigate to "Reporting & SCA" > "Licenses" > and select "Manage License Types & Rules".
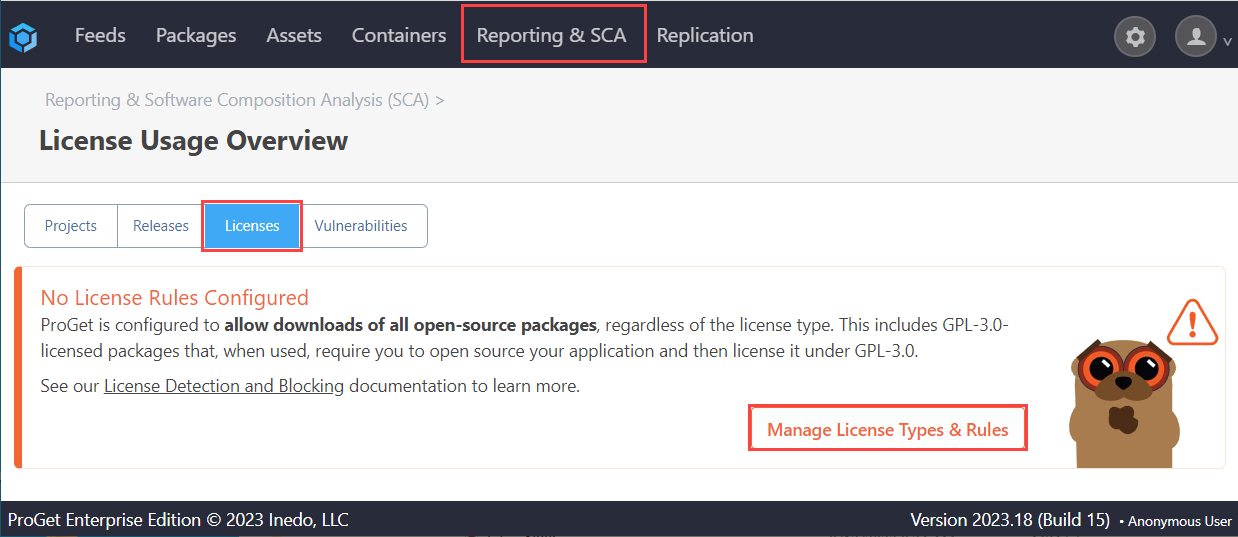
From here we want to locate the "GPL 3.0" license:
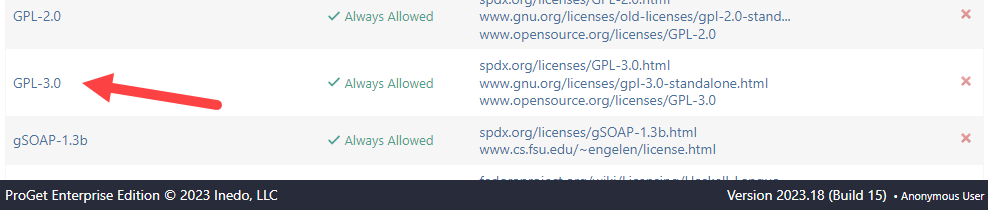
From here you can view the license agreement and decide if it needs to be blocked. Selecting the license, you can view the definition, including the license code and SPDX identifier:
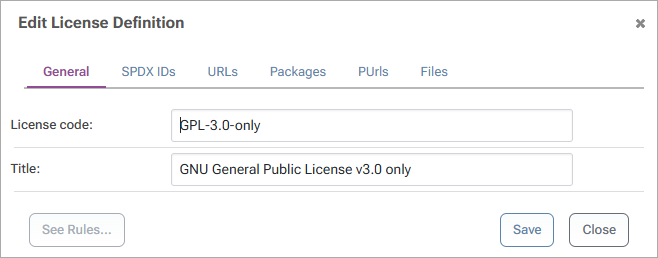
Step 2: Block License
From this window, select "See Rules..." then global to head to the Global Policies page where the license can be blocked:
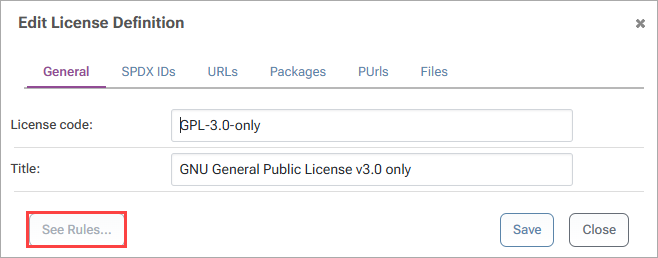
Now select "edit licenses":
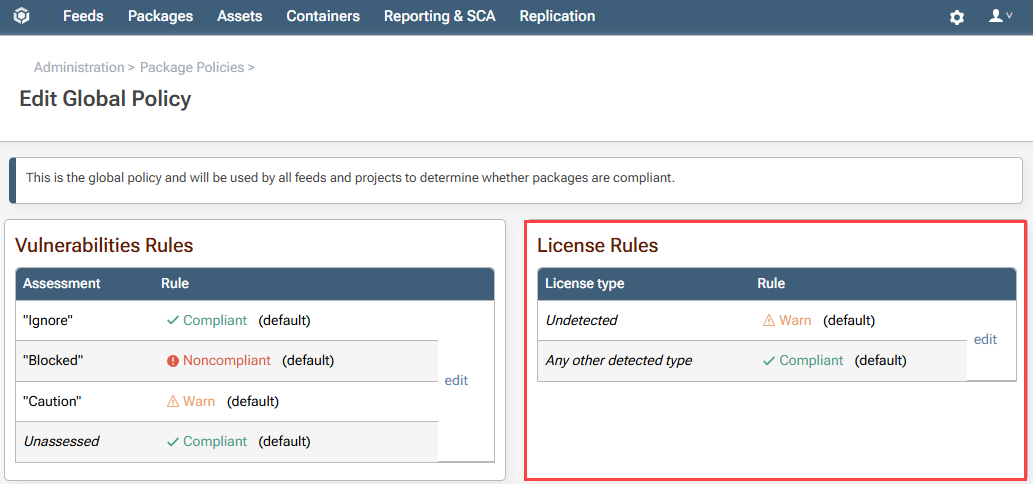
From the Edit License Rule window select the Noncompliant tab, search for the GPL 3.0 license, and select "Save".
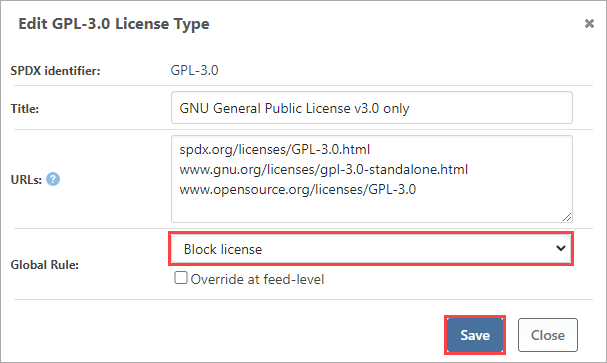
This will prevent GPL 3.0 from being downloaded or used from any feed in your ProGet instance.
Step 3: Confirm Restriction
To confirm this, we will take a look at "Accord.MachineLearning 3.8.0", which uses the GPL 3.0 license. Navigate to "Feeds" and select a NuGet feed. For this demonstration, we will use a feed we have created named public-nuget. From here search for "Accord.MachineLearning" and select the relevant package.
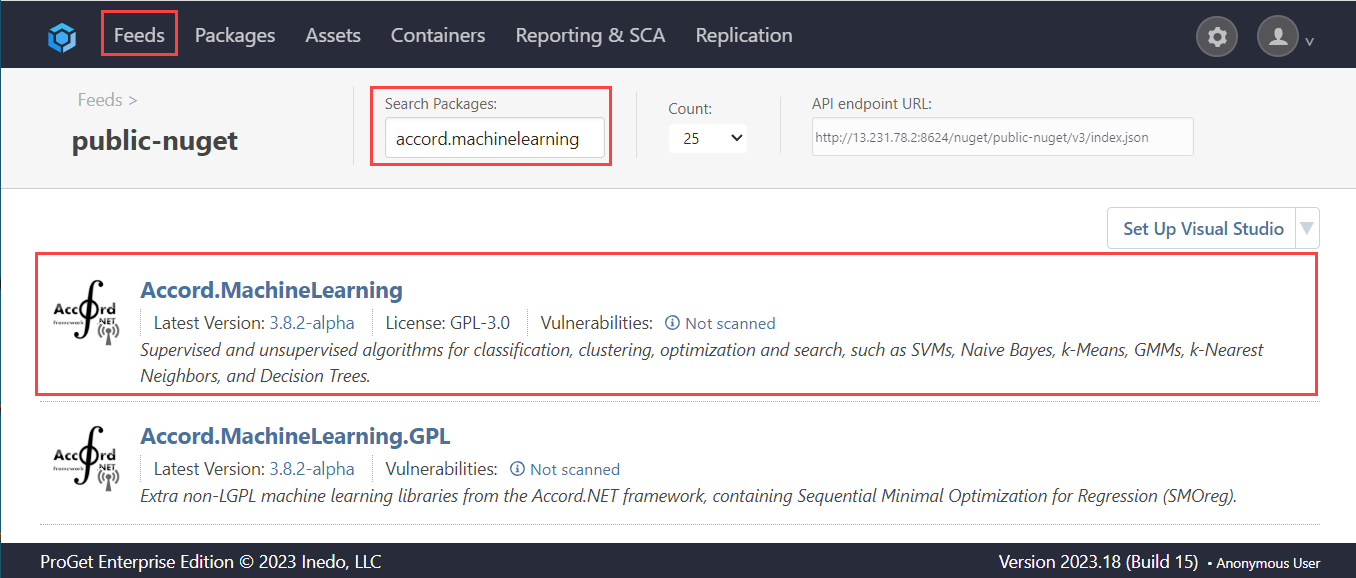
We can now see that it is blocked as a result of our actions.
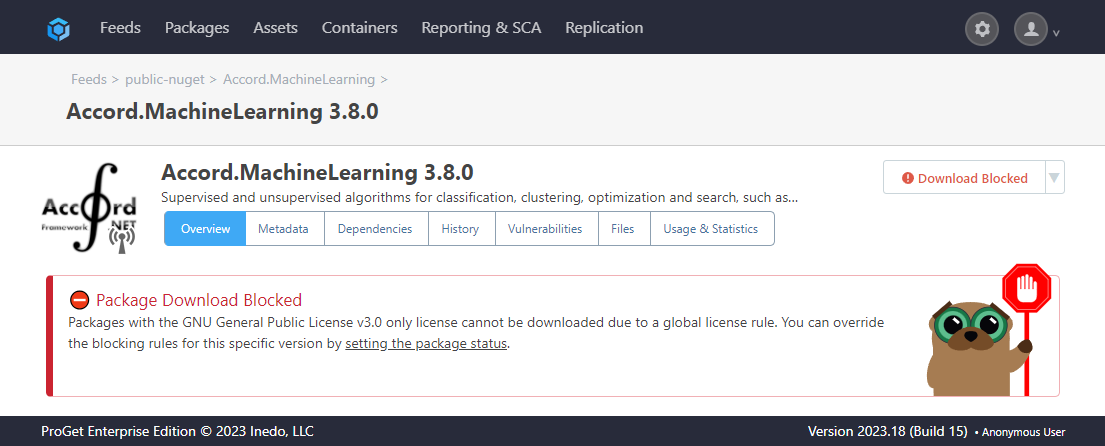
Overriding at Feed Level
Overriding at feel level allows us to configure unique rules for feeds of our choosing. In this case, it will allow us to permit the downloading and use of packages using licenses that have otherwise been blocked globally.
In this scenario, "Project ABC," which uses a nuget-project-abc NuGet feed, is licensed under GPL 3.0. Therefore, packages licensed under GPL can be approved for use in this project.
Navigate to your feed then to the Policies and Blocking tab and select "edit License Rules":
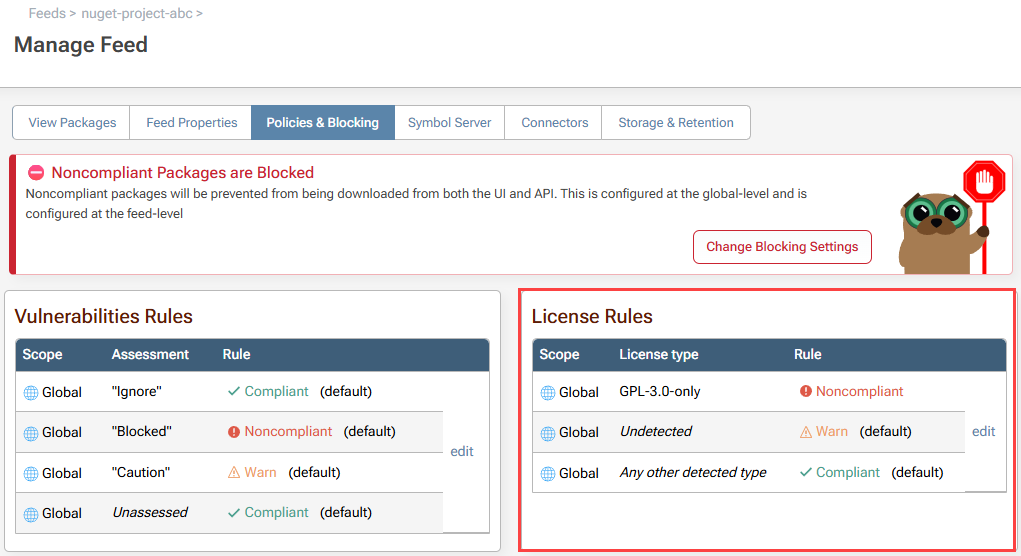
To change the rule scope to the nuget-project-abc feed, select change, then select the feed:
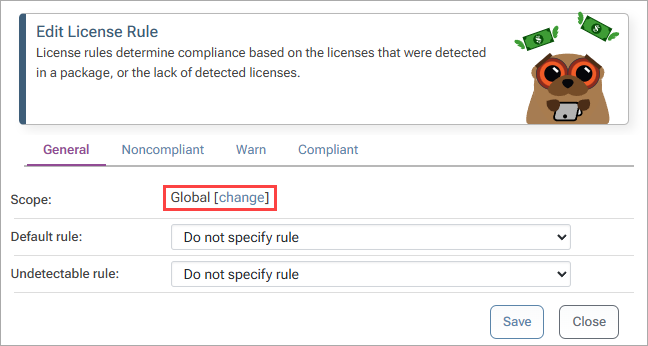
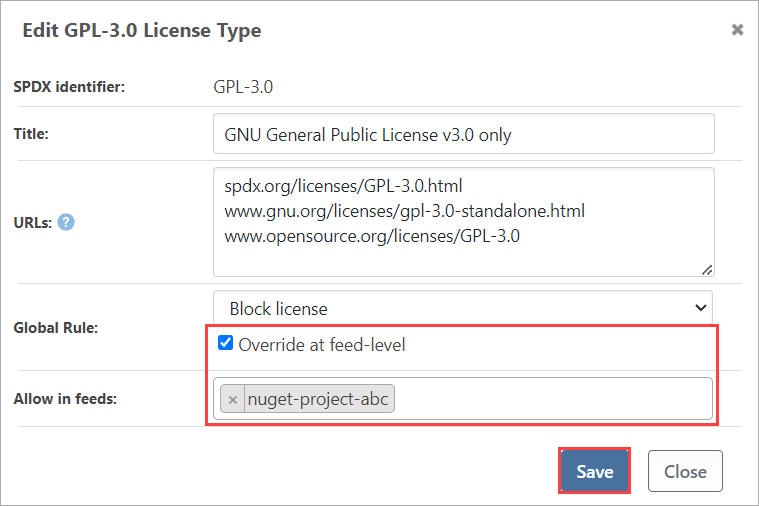
Now add the GPL 3.0 licenses to the Compliant list. This will permit downloading and use of packages that use the GLP 3.0 license.
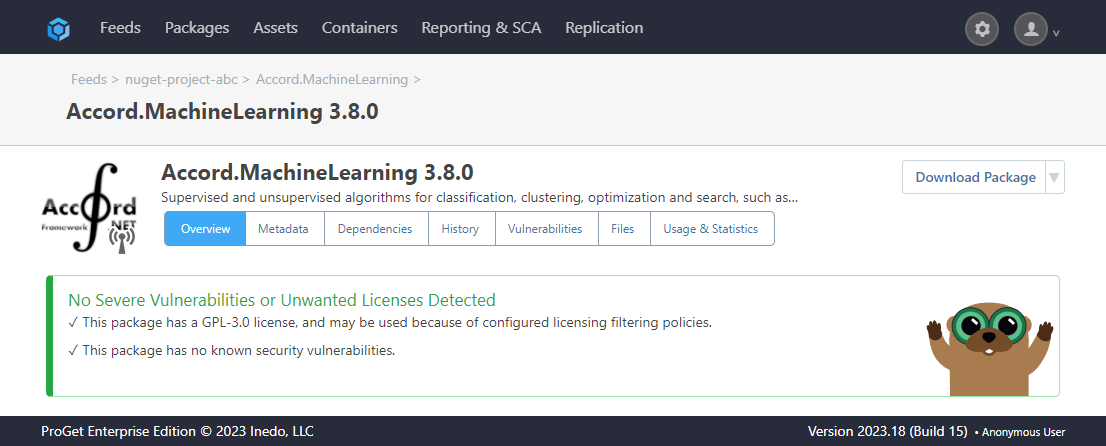
We can confirm this by navigating to the nuget-project-abc feed and selecting the "Accord.MachineLearning" package. We can now see that it is allowed as a result of our actions.
How to Allow only Specific Licenses (Whitelisting)
In this scenario we want to take a list of licenses, begin by blocking them globally, and then decide on licenses we want to allow, permitting downloading and production use. We'll start with the "MIT" license as it's generally regarded as acceptable.
Step 1: Block All Licenses by Default
In ProGet, all licenses are allowed by default when a feed is initially set up, so we will need to change this first. Start by navigating to "Administration" > "Package Policies and Rules" > "edit Global" > and selecting "edit License Rules".
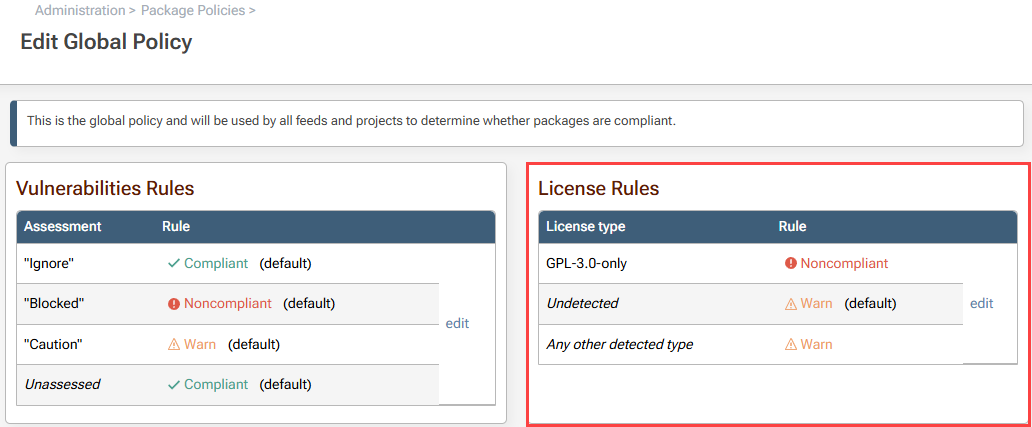
From here set all licenses to be Noncompliant by default.
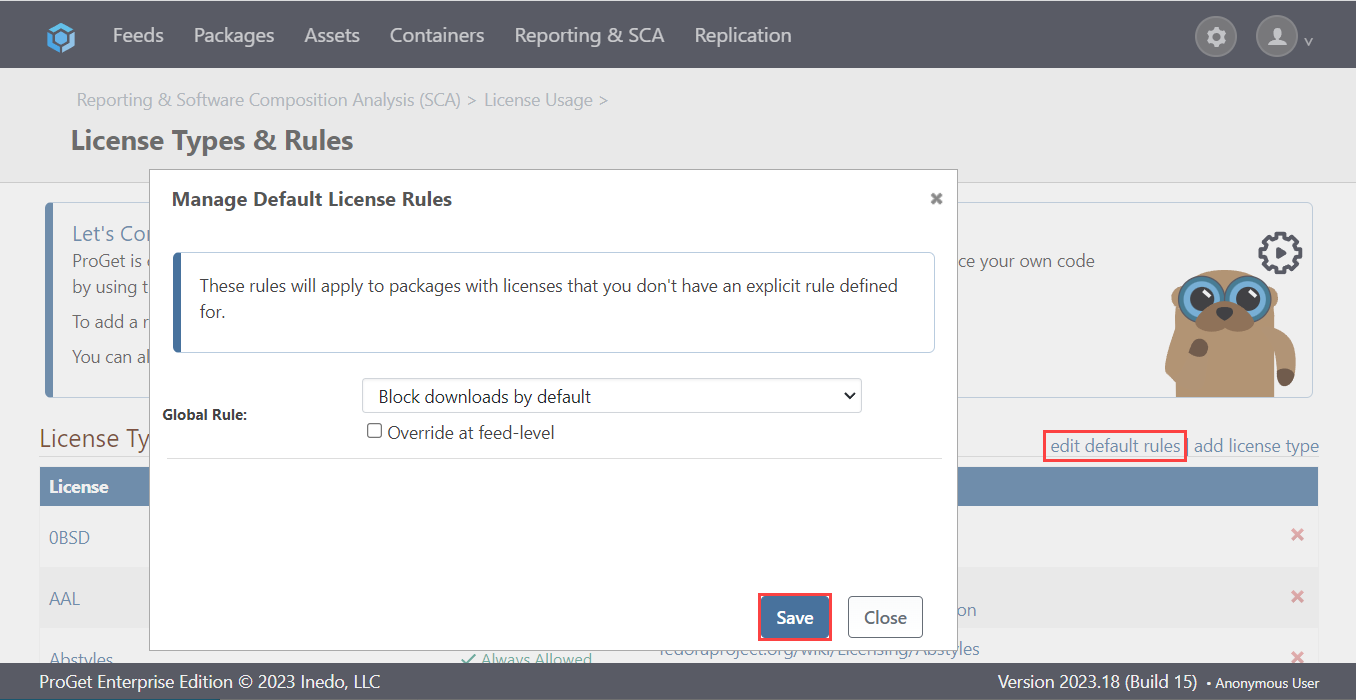
Navigating back to Manage License Types & Rules, you will now see that all licenses listed are blocked by default.
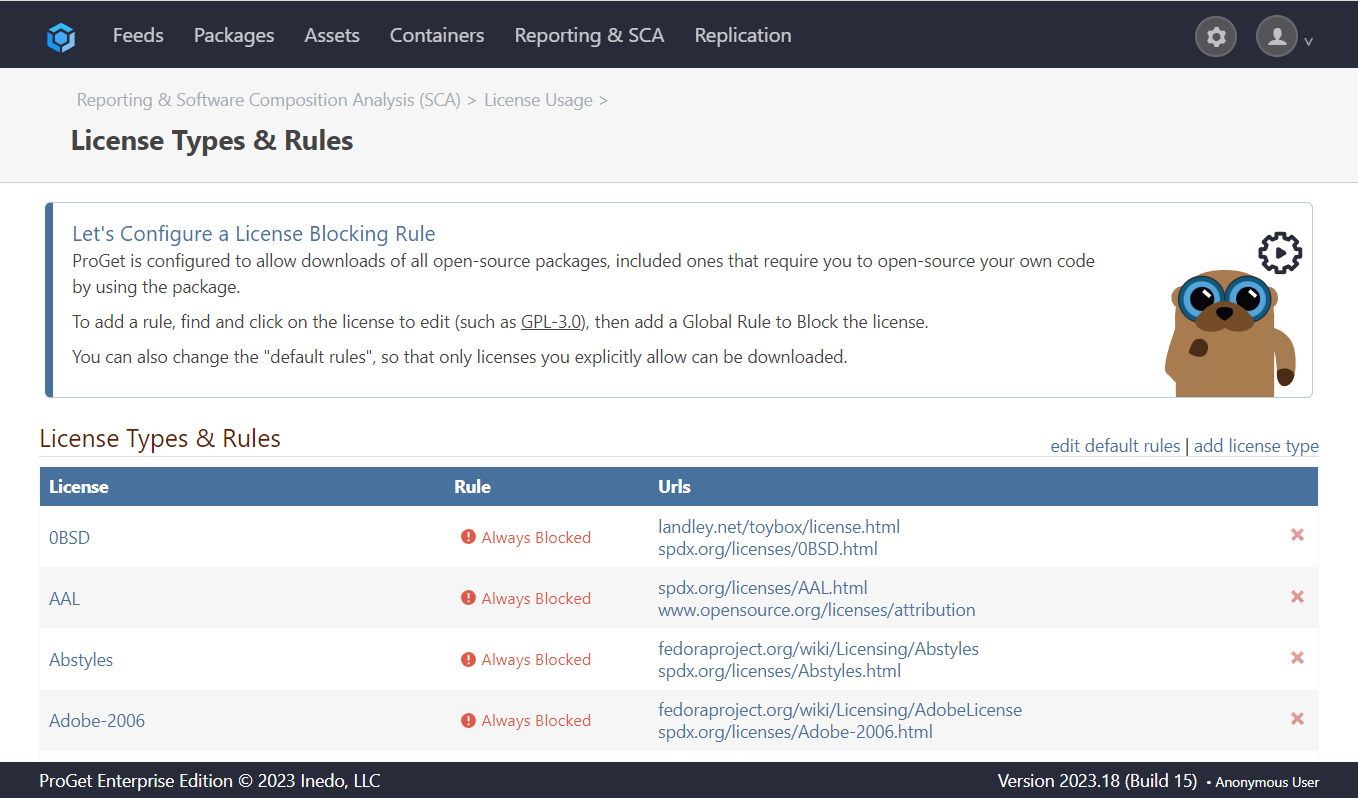
Step 2: Allow License
Next, we will allow the MIT license. From the licenses edit License Rules menu in Global Policies find the "MIT" license in the Compliant tab and select "Save".
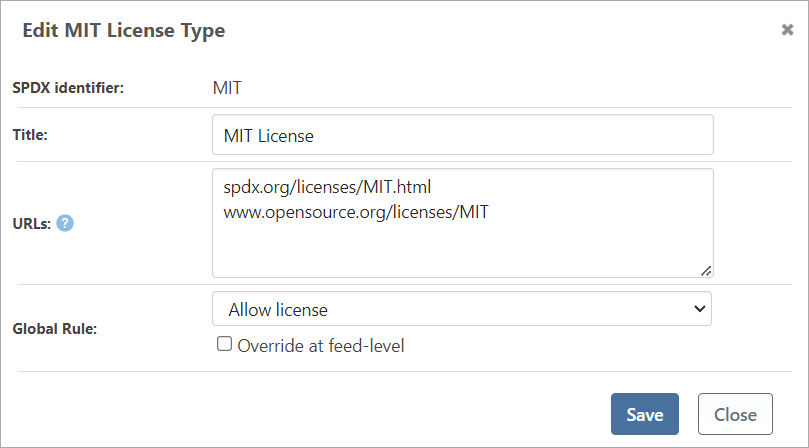
This will allow packages with the MIT license to be downloaded and used.
Step 3: Confirm Permission
To confirm this, we will take a look at "Newtonsoft.json", which uses the MIT license. Navigate to "Feeds" and select a NuGet feed. For this demonstration, we will use a feed we have created named public-nuget. From here select the "Newtonsoft.json 13.0.4" package, which will normally be one of the first in the feed, or search for it if necessary.
We can now see that it is allowed as a result of our actions.
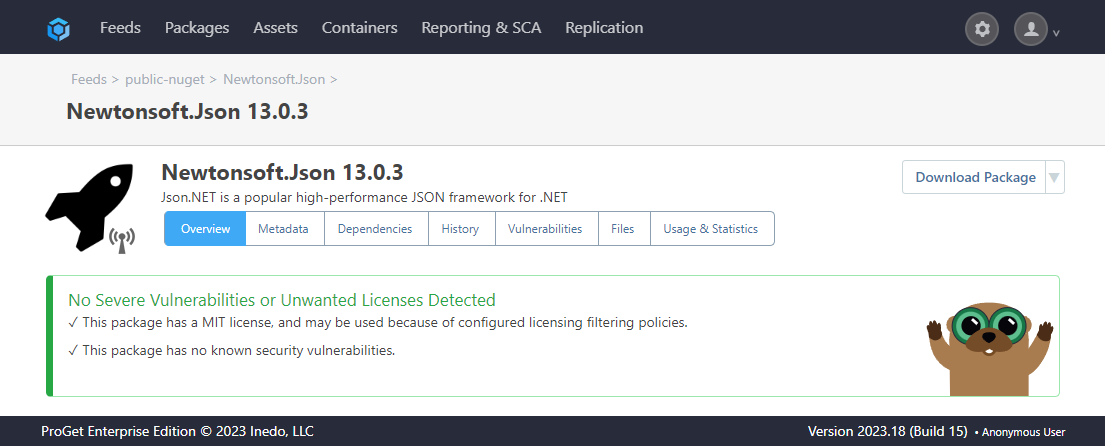
Overriding at feed level
In the same way as detecting and blocking above, overriding at feel level is possible when allowing approved licenses. In this case, it will allow us to prohibit the downloading and use of packages using licenses that have otherwise been allowed globally.
In this scenario, GPL licenses are globally approved. However, for "Project XYZ," which uses a nuget-project-xyz NuGet feed, is explicitly prohibited from using these licenses. Therefore, the "GPL 3.0" license must be blocked for this particular project.
Navigate to the Polices & Blocking tab of the feed, in this case nuget-project-xyz, and select "edit License Rules".
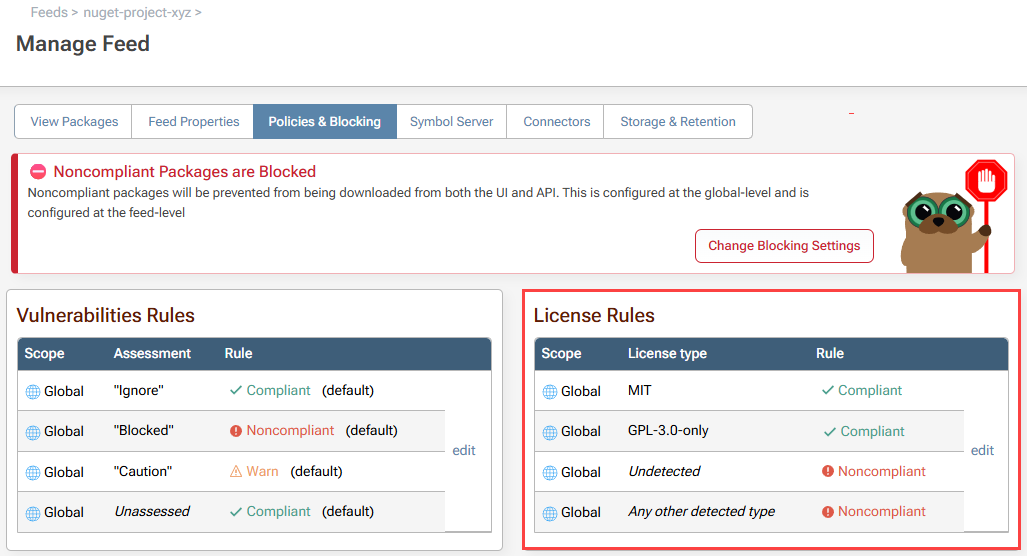
Change the rule scope to the feed in question:

In the Noncompliant tab search for the "GPL 3.0" license, and select "Save". This will block downloading and use of packages that use the GPL 3.0 license in this feed.
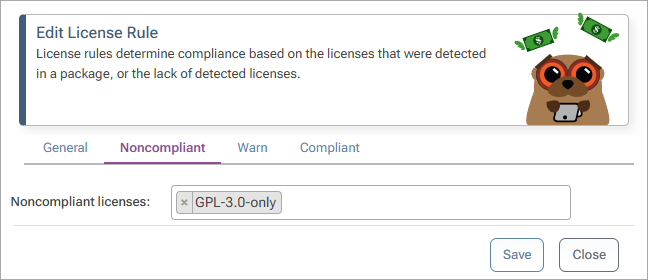
We can confirm this by navigating to the nuget-project-xyz feed and selecting the "Accord.MachineLearning" package.
We can now see that it is blocked as a result of our actions.
Section 3: Troubleshooting
What if a Package Has No License?
When handling packages in a feed, you may experience two cases of packages without any assigned license.
Case 1: URL-Based Licenses
These are packages with URL-based licenses. An example of this is "Aspose.Words 25.11.0". When viewed in ProGet, it will appear like this:
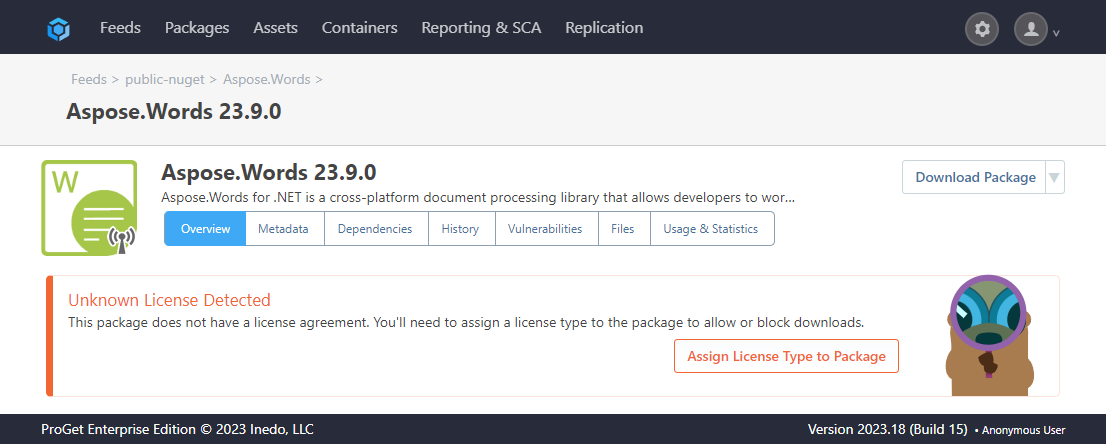
For these packages, you will need to access their related website to view the license.
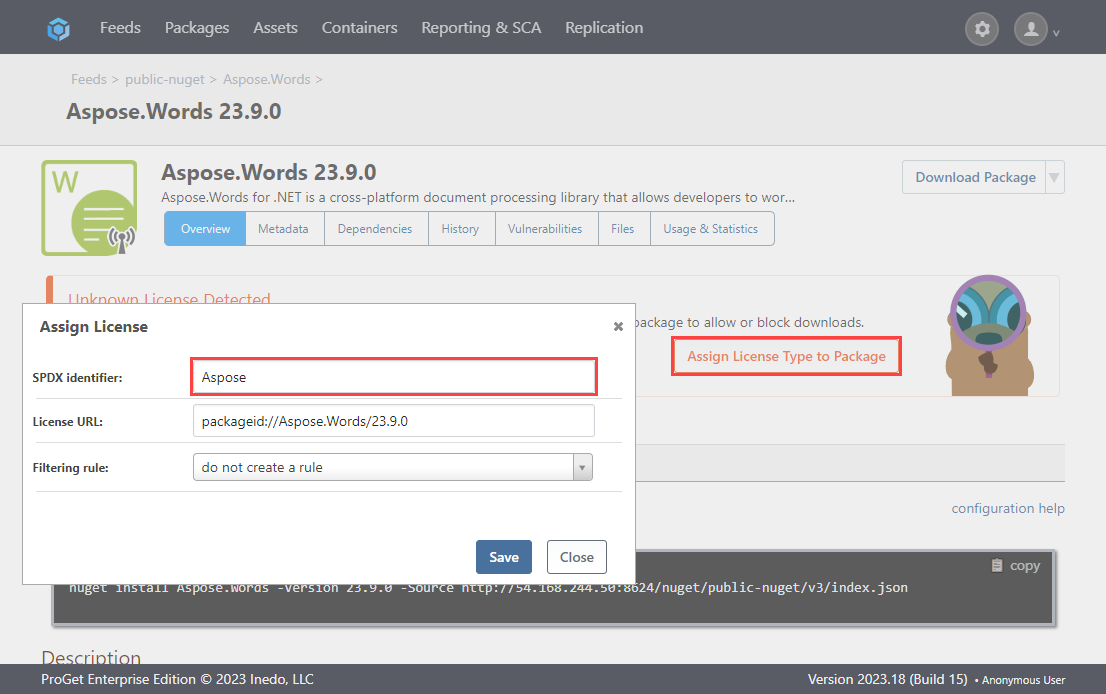
In this case, "Aspose.Words" has it's own license, meaning you will need to assign it a custom license in ProGet. Do this by selecting "Assing License Type to Package".
Select Create New License, then type in a name for the license and select "Assing License".
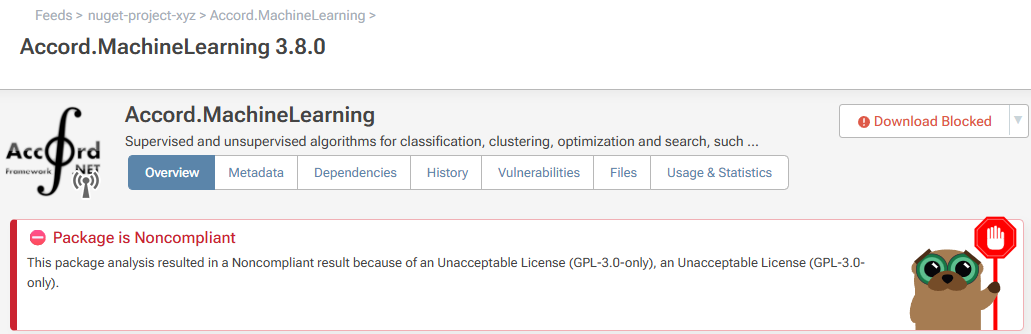
Case 2: Embedded Licenses
These are packages with embedded licenses. An example of this is " Accord.MachineLearning 3.8.0". When viewed in ProGet, it will appear like this:
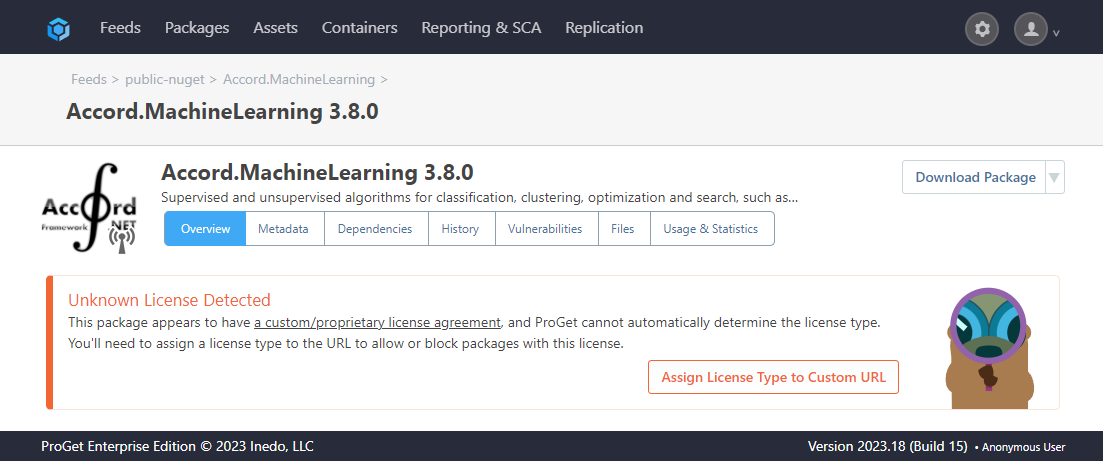
For these packages, you will need to view the license via the link on it’s page.
Here it states that it uses the "GPL 3.0" license.
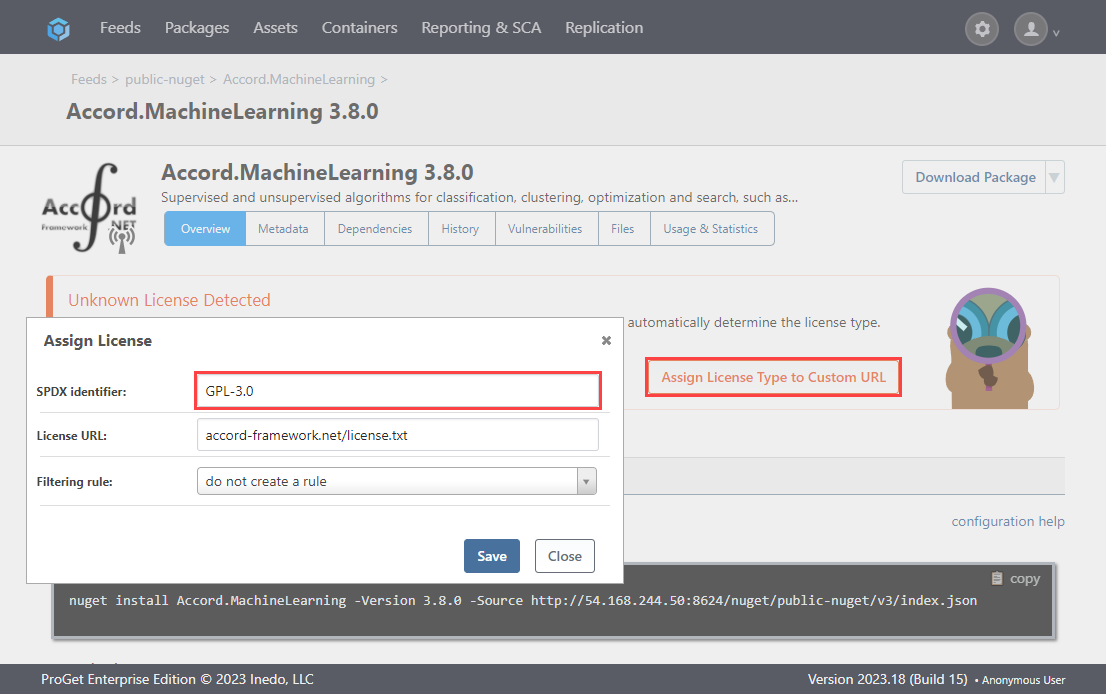
Select "Assign License Type to URL", then search for "GPL 3.0" from the list and select "Add License".

