What is a "server" in Otter?
Otter works with both Windows and Linux servers as well as physical (bare metal) or virtual servers, hosted in your own datacenter or in the cloud. A "server" in Otter is essentially a connection to one of your servers, wherever it may be.
Once you have prepared your server for Otter, you will be able to:
- Monitor configuration drift
- Manage your current and desired configuration
- View installed packages and containers
- Review history of jobs and changes to server
- Configure server variables
- Mange your servers and environments
Preparing Your Servers for Otter
Otter can communicate with servers that have the Inedo Agent installed or use "agent-less" communication with PowerShell remoting (WMI) or with SSH.
Installing the Inedo Agent (Recommended)
The Inedo Agent was designed expressly to communicate with Inedo products, offering:
- Both inbound and outbound communication (simplifying router and firewall configuration across networks)
- Easier configuration
- Optimized performance with Otter
- Lower permissions with less chance of attack than WMI or SSH
To install the Inedo Agent, you can follow our step-by-step guide for the GUI-based installer or use more advanced options like silent installation or manual installation.
Connecting with WMI (PowerShell Remoting)
Otter can also use WS-Management (WMI). This is the same channel that PowerShell remoting uses and is available only on the Windows platform.
The easiest way to enable is using Enable-PSRemoting cmdlet, as follows:
Enable-PSRemoting
This command does many things, including:
- Configure the WinRM service used for WMI communication
- Create a listener to accept requests on any IP address
- Enable a firewall exception for WS-Management communications.
- Change server security to allow remote access
After enabling WMI, Otter will be able to connect to the server using a local Windows or domain account.
Troubleshooting
If Otter reports back an error when running a script or orchestration that looks like this:
WinRM cannot process the request.
The following error with error code 0x8009030e occurred while using Negotiate authentication:
A specified logon session does not exist. It may already have been terminated.
This happens becasue the Otter Service does not trust the remote PowerShell host. To fix this, run the following PowerShell on your Otter Server:
Set-Item -Path WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value 'REMOTE_SERVER_NAME'
Connecting with SSH (Linux)
To communicate with Linux servers, Otter uses SSH and SFTP, which nearly every Linux server already has enabled. Otter can use a private key or username/password to connect.
Adding Your Servers in Otter
Once your server has been prepared, you can add the server by going to Servers > Add Server, or you can use the infrastructure API.
The “Add Server” menu in the Otter UI will present you with three different options for the agent/communication type:
- Inedo Agent: Connects to an Inedo Agent that is installed and listening on a remote server
- PowerShell: Connect to the remote server using PowerShell remoting
- SSH: Connect to the remote server using SSH (Linux-only)
Monitoring Configuration Drift
Otter can monitor servers for configuration changes and report when there's configuration drift. Server rolse are used for defining sets of configurations that can be assigned to any number of servers.
For example, you may have an iis-server role that ensures IIS is configured in a particular way, as well as an foobar-api-host role that ensures a particular web application is configured properly. Both roles can be applied to the same server so that foobar-api-host is configured on an IIS server.
Assigning Roles to Servers
When server roles are assigned to a server, Otter can use the OtterScript configurations of those server roles to collect and compare that server's current (actual) configuration against the desired configuration (defined by the server roles) and report any differences as "drift."
You can assign roles from the server page ("assign role") or from the server role page ("assign servers").
Configuration Drift Setting
When "Detect configuration drift" is set, you have three options:
- Do not remediate (report only): just lets you know a server has drifted
- On-demand or scheduled remediation: uses a configuration job to remediate drift on-click or at a certain day/time
- Immediately upon detecting drift: automatically remediates drift when detected, no matter when or what
Current and Desired Configuration
Configuration drift is when a server's actual configuration is different than the desired configuration. It can occur expectedly (e.g., if you change the configuration plan) or unexpectedly (e.g., someone manually made a change on the server).
Navigate to Servers > Server Name > Desired Configuration tab to see the OtterScript that is generated by combining the OtterScript configurations of a server's roles and is what will be used to compare each role’s desired state with the server's current configuration.
Click to the “Current Configuration” tab on that same screen to see the current configuration, which will indicate “Current” with a green checkmark or indicate “Drifted” with an orange forked line.

Installed Packages and Containers
Otter can automatically collect information about the following packages types on a target server:
- Debian Packages
- Docker Containers
- DSC Modules
- PowerShell Modules
- RPM Packages
- Universal packages
To learn more see Collecting Containers and Packages
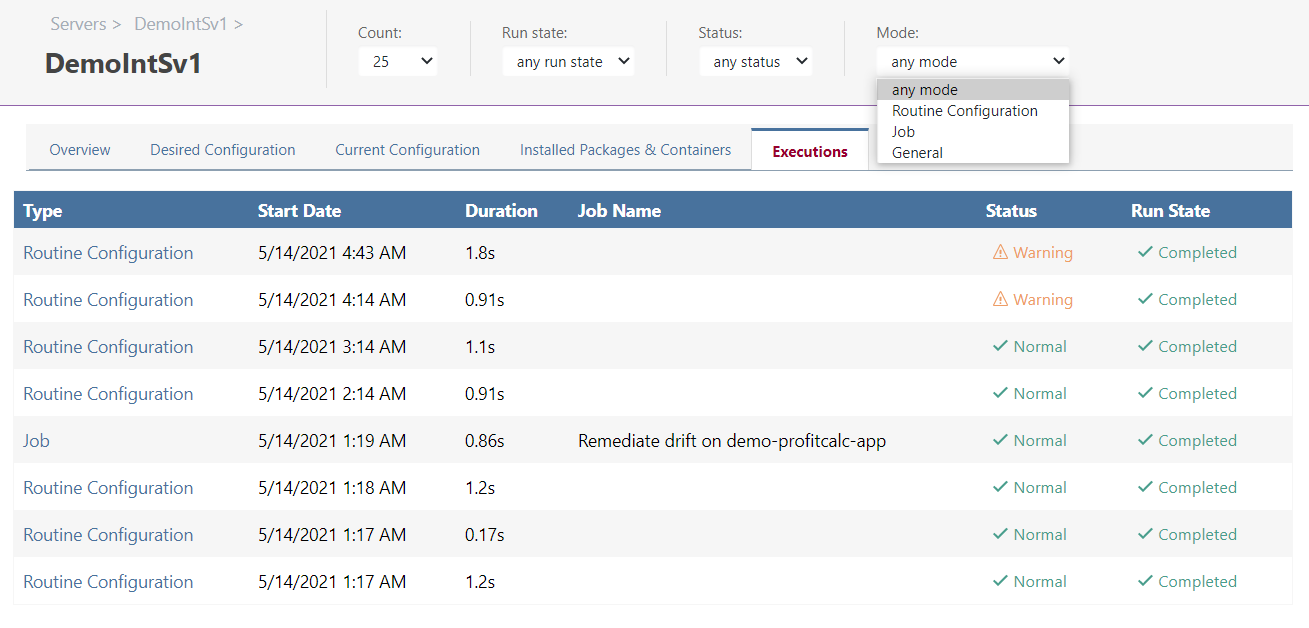
History of Jobs and Changes to Server
Executions tab shows recent executions off all jobs and routine configurations, along with detailed information such as the status (normal/error) ad duration
You can use filters to only display certain types of events. This helps with tasks such as identifying errors, especially if there is a long list of executions.
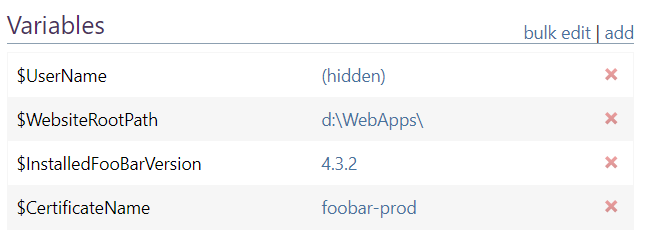
Server Variables
Server variables are configuration variables that will be automatically be used in the OtterScript that runs against the target server. These configuration variables will be cascade on top of any global configuration variables, but only for the server, they are defined on.
Server variables can be created and modified on the "Overview" page of a given server.
Servers and Environments
Servers, Status, Environment, and Roles can all be viewed in table-form by navigating to “Servers.” Clicking into each server, the “Overview” page displays details about the server.
In Otter, Environments are a logical grouping of Servers, and generally describes one stage of the development process (development, testing, Q/A, production, staging, etc). To change the environment of a server, edit the details tab.
You can associate one server with multiple environments, but this is not recommended as it can lead to unexpected behaviors.

