Desired Configuration with OtterScript
Otter helps you to define a "desired configuration" for your servers that can include anything from registry settings to firewall configuration to an application pools and websites within IIS. Otter will then routinely collect information this configuration and tell you if your servers' configuration matches the desired configuration.
Defining this desired configuration doesn't require any programming skills; OtterScript is accessible to both coders and non-coders with OtterScript’s visual and text modes. In visual mode, you can simply drag-and-drop items to define your desired configuration, and switch back-and-forth to text mode as needed.
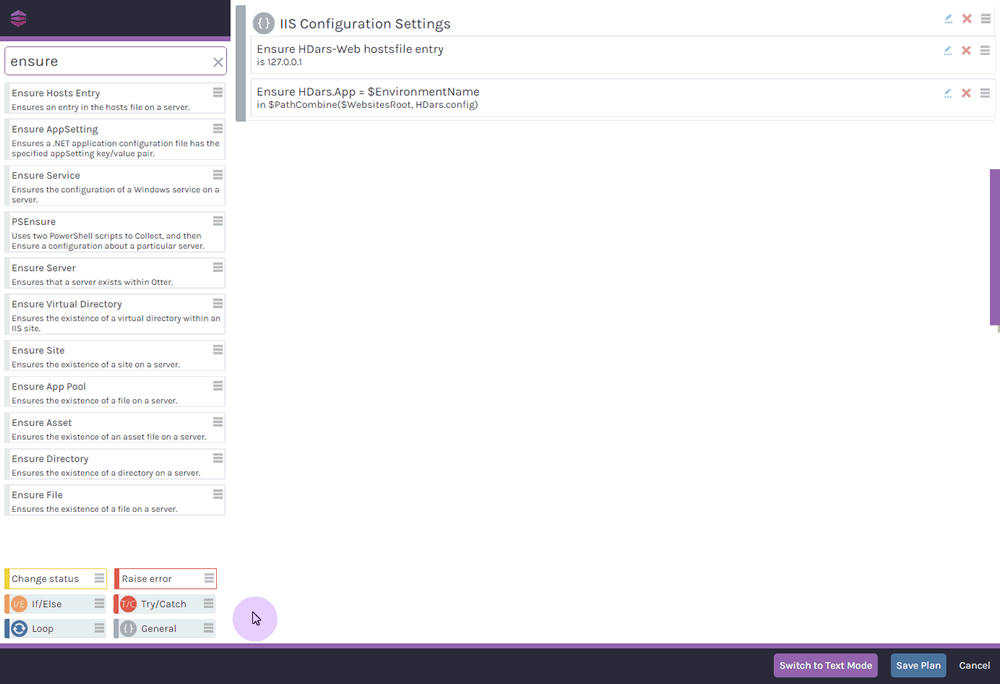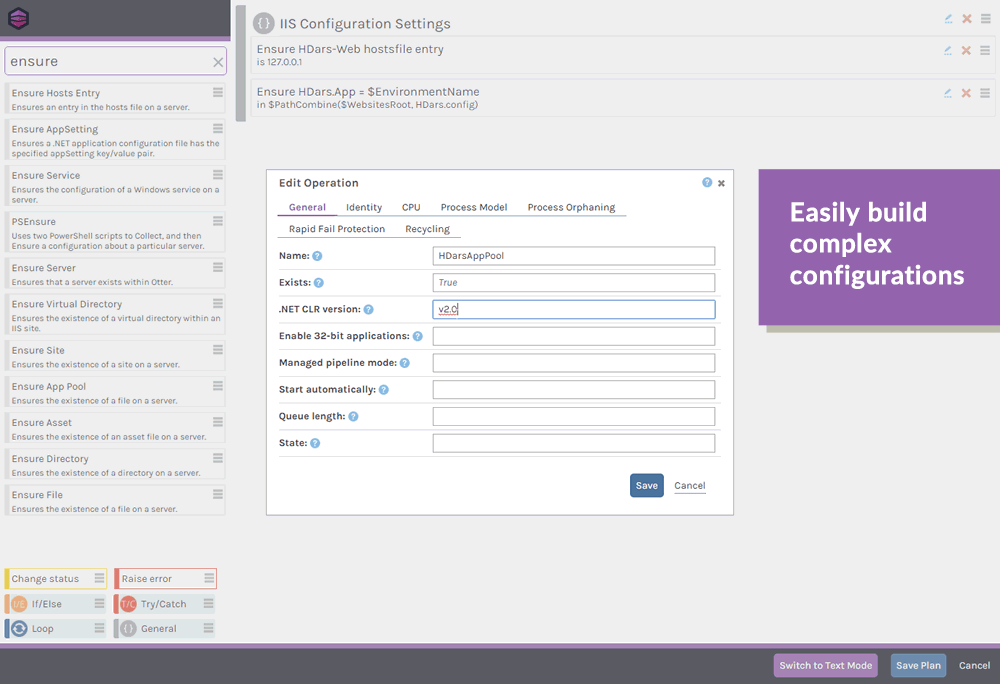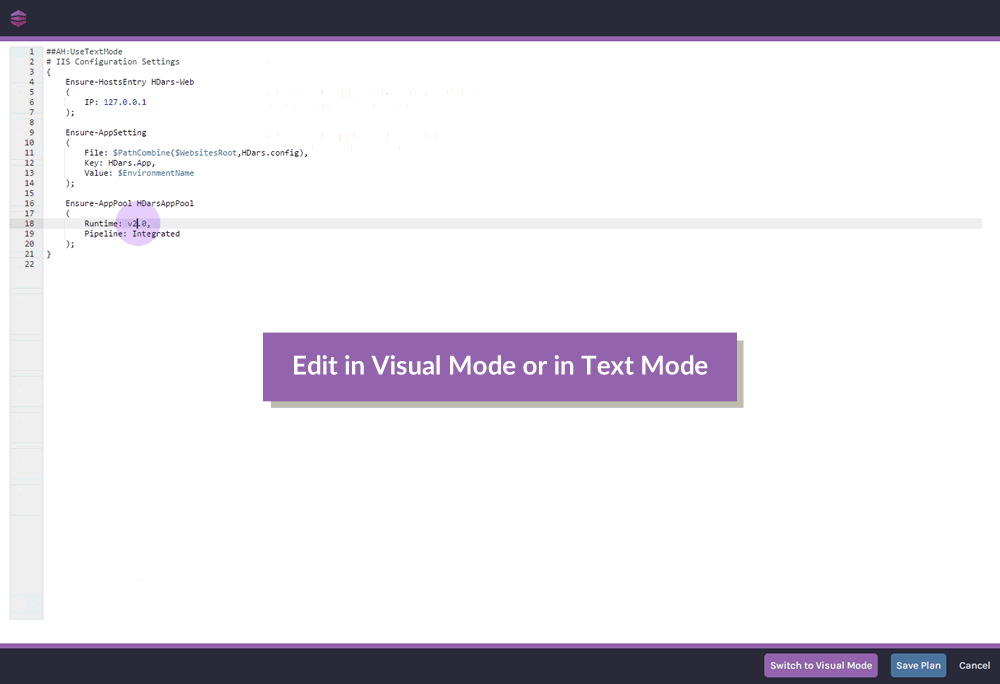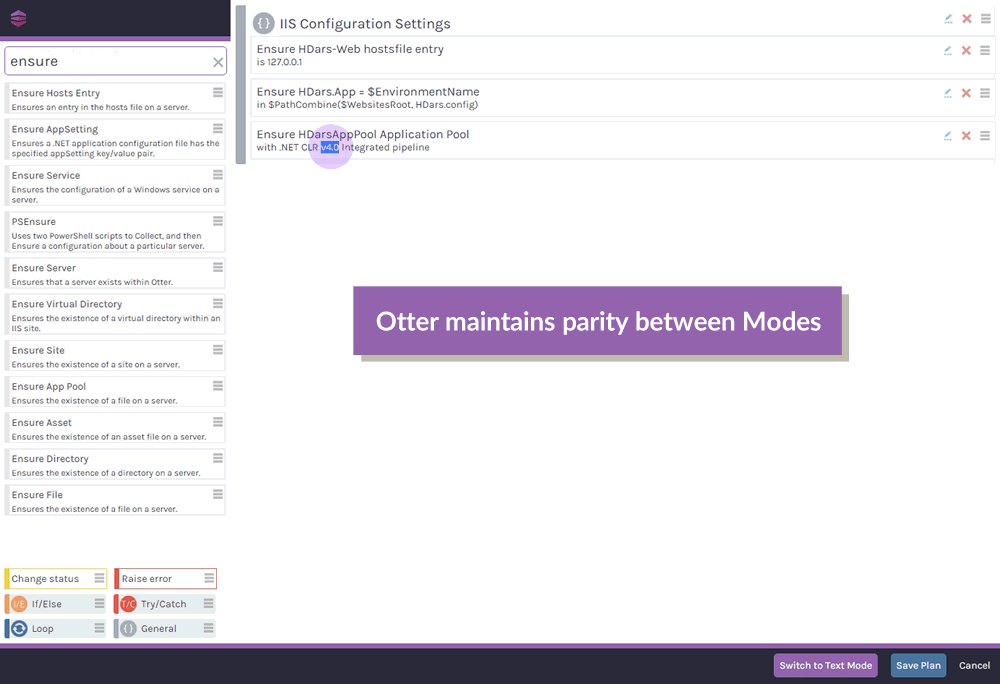
This level of flexibility is designed to make Otter accessible to both beginners, and seasoned administrators.
NOTE: Don’t confuse “Desired Configuration” with PowerShell DSC – they’re not the same thing, but you can certainly use PowerShell DSC when you define a desired configuration in Otter.
What is "Configuration" in Otter?
"Configuration" refers to anything you do to a server (i.e., your infrastructure) after a fresh install of the operating system. On Windows, this includes things like:
- Adding Windows Features, such as IIS
- Creating an Application Pool
- Opening a port on the Windows Firewall
- Installing a Windows Service
Because configuration can involve thousands of small changes (especially after operating system updates), Otter only collects information about your desired configuration, and then shows that on the "Current Configuration" tab on a server.
Example: Firewall Desired Configuration
For example, your desired configuration included firewall rules, Otter would display the state of each firewall rule as follows.
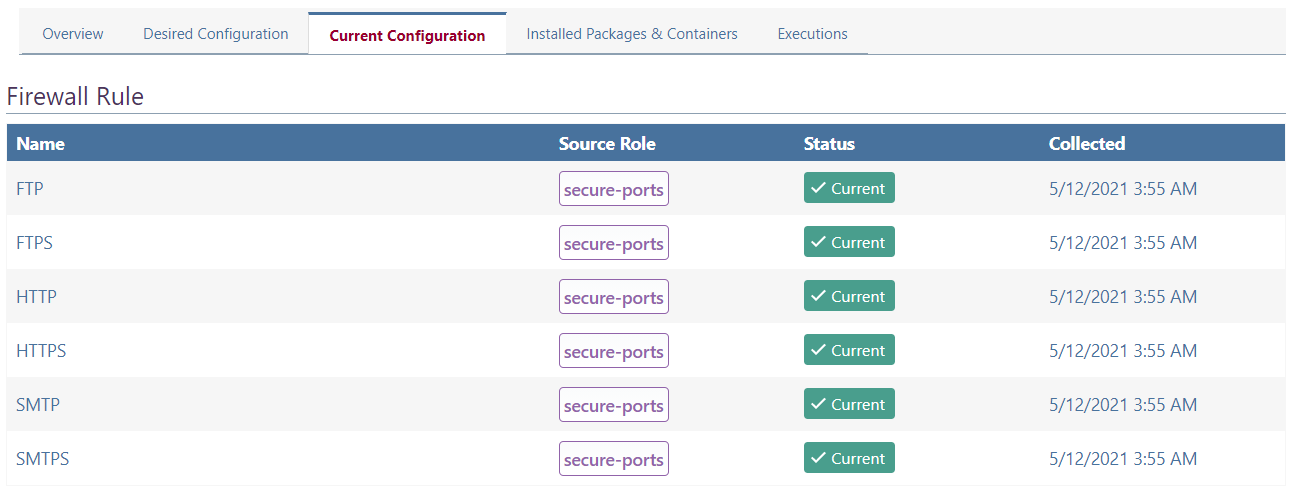
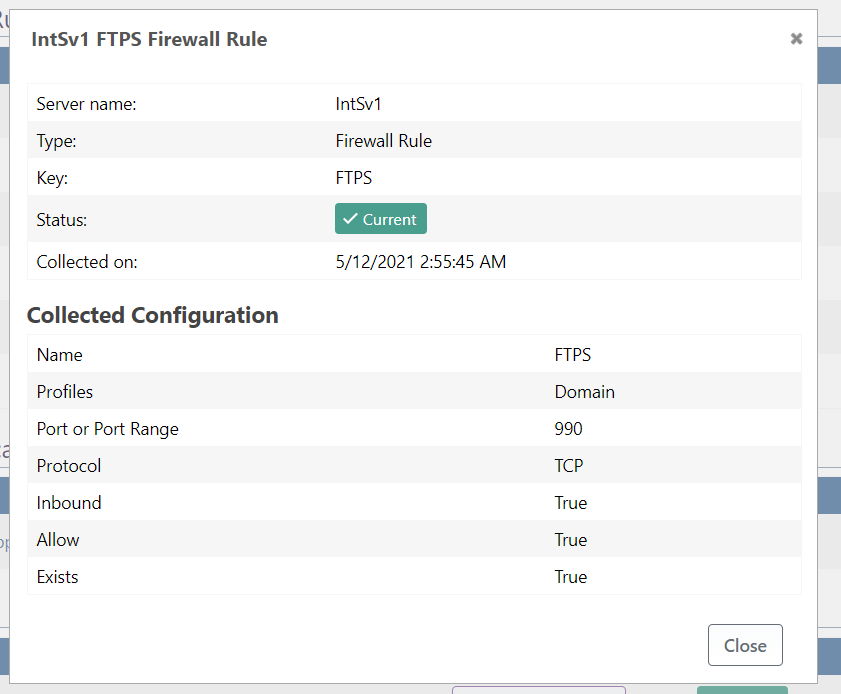
You could get more information about the collected details by clicking on one of the pieces of configuration:.
Automatic Configuration Collection
Otter will routinely scan all the servers you've added, and compare their current (actual) configuration against the desired configuration you've defined. By default, this is done hourly, but you can change this setting under Admin > Advanced Settings, and setting Execution.RoutineConfigurationExecutionThrottle.
You can also manually scan a server by navigating to that server, and then clicking "Check Configuration". You can scan all of the servers in particular server role in the same manner.
To trigger a scan of all servers in Otter, navigate to Admin > Manage Service, and run the Routine Configuration task runner.
You can also programmatically check configuration and detect drift using the configuration management API.
Desired Configuration and Configuration Drift
"Configuration Drift" is what happens when a server's current (actual) configuration is different than its desired configuration.
Drift can occur from manual changes (i.e. someone logging into the server and changing it) or automated processes (such as a Windows update) changing the server's configuration.
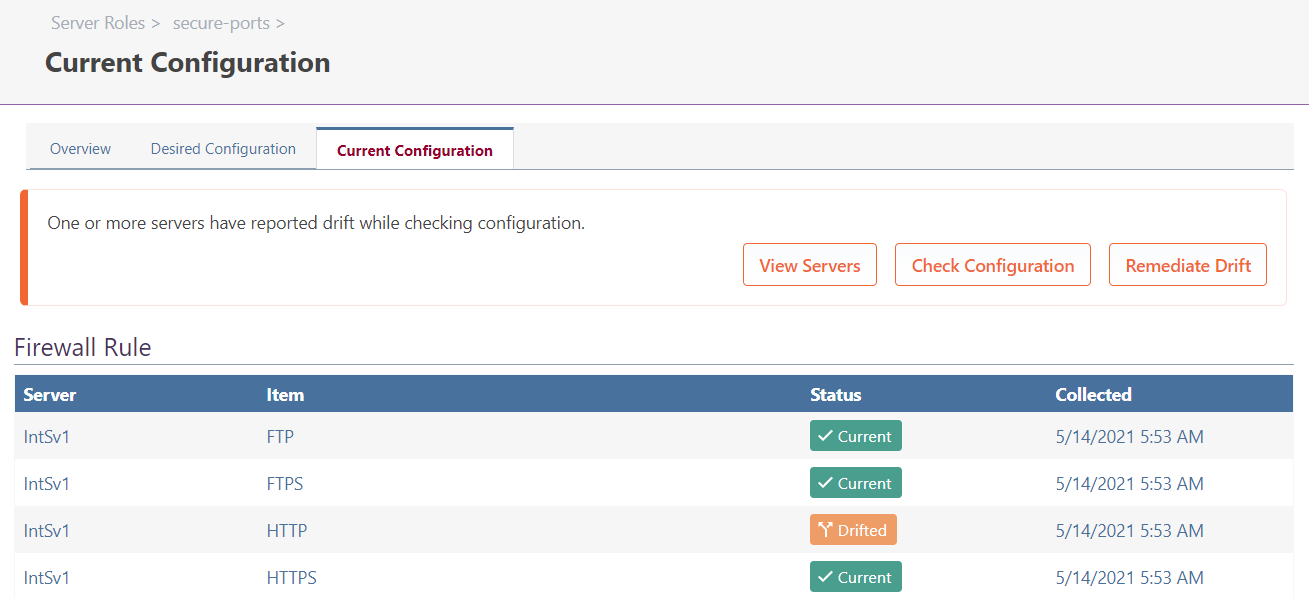
Example: Drifted Firewall Rule
For example, let's say your server's desired configuration was that a HTTP Firewall Rule should be defined to block port 80. But on the server, the HTTP Firewall Rule said just the opposite: that port 80 was allowed. In this case, that configuration item will be considered drifted.
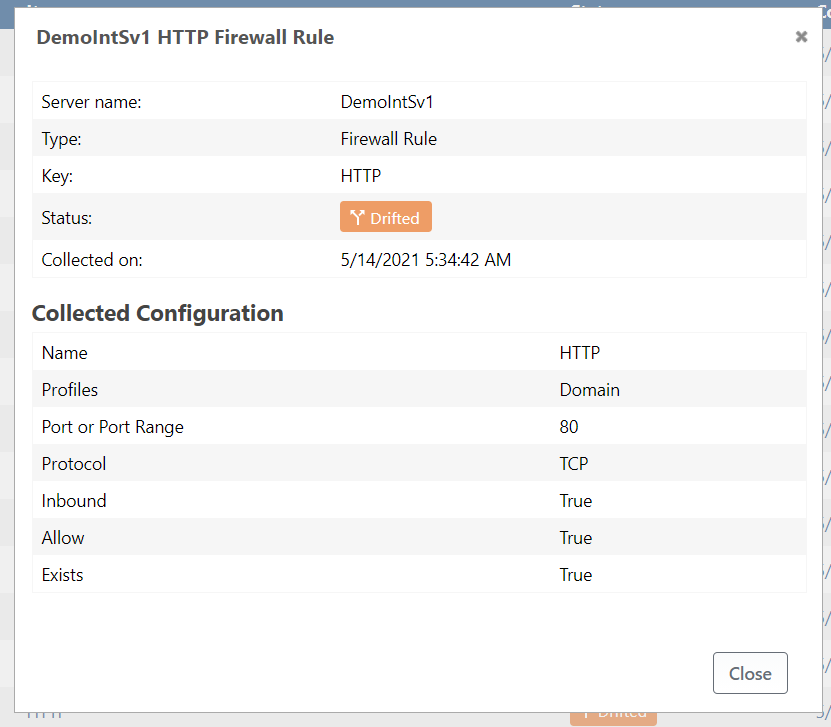
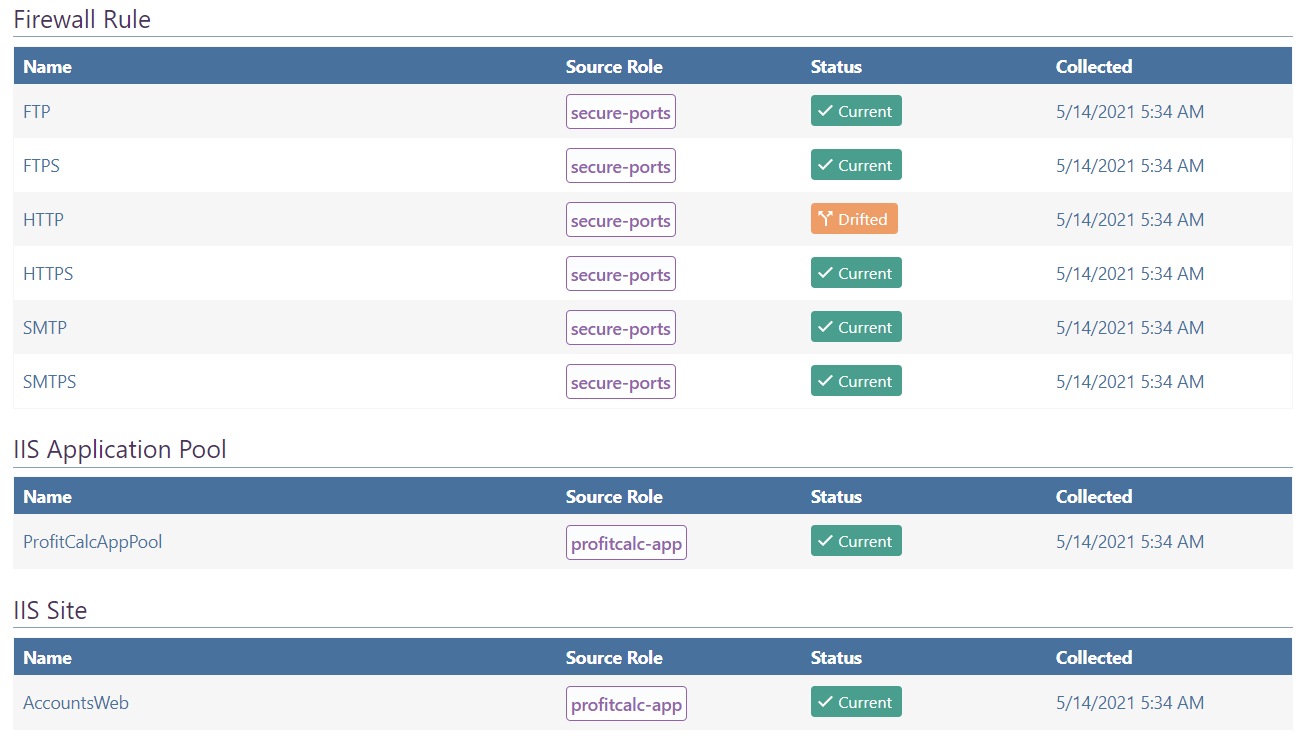
You will easily be able to spot this "Current Configuration" tab of a server, as well as which server role the drift is coming from.
What is a "Drifted" server?
A server is considered to be "drifted" state if any one piece of desired configuration doesn't match the current (actual) configuration. You can see which servers are drifted by navigating to Servers, and selecting Drifted from the status filter.
What is a "Drifted" Server Role?
A server role is considered to be "drifted" if any server assigned that's assigned that role has a drifted configuration item from that role. For example, let's say you have two server roles defined: secure-ports and profitcalc-app.
The secure-ports role will be considered drifted if any one of the servers is missing (or has an improperly defined) port.
You can see which specific configuration item on which server is causing drift by navigating to the Current Configuration tab of the Server Role.
What is a "Drifted" Environment?
Environments are considered drifted if any single server in that environment is drifted.
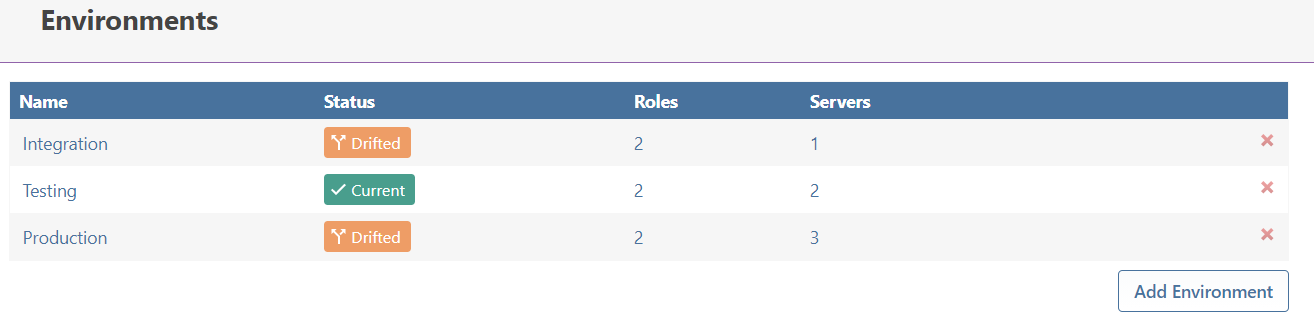
You can see which specific server is drifted by clicking on the Servers button on the Environments page.
Detailed Configuration Collection & Drift Detection
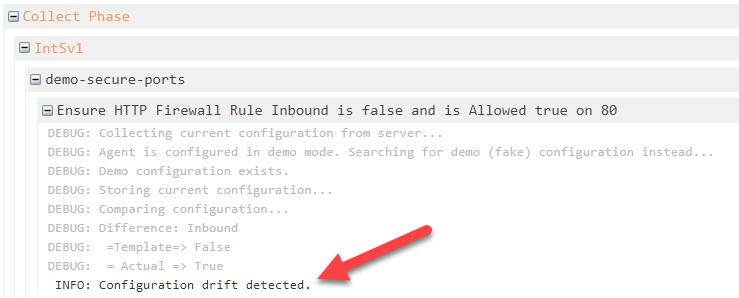
Otter maintains details logs that can show you exactly how and when current (actual) configuration was compared against the desired configuration. This may help you troubleshoot why configuration is, or isn't drifted.
The execution logs are available on any of the Current Configuration tabs by clicking on the date next to the piece of drifted configuration. If you expand the log scopes, you'll be able to find the precise item that triggered configuration drift.
How to fix (Remediate) Configuration Drift?
The most common way of fixing configuration drift is to log-in to the server, and change the current (actual) configuration to the desired configuration. But that can be pretty tedious, especially if you have a lot of servers.
Otter can also do this at the click of a button! See Automatically Remediate Configuration Drift to learn more.
Configuration as Code with OtterScript
Treating configuration the same as code is at Otter’s heart. OtterScript is particularly helpful, as it is a low-code scripting language. The low-code visual mode is accessible and usable by even non-coders, while the text editor allows coders to work in their preferred manner.
OtterScript & Operations
Just about everything in OtterScript is accomplished through Operations, and that includes defining your desired configuration.
Whether it's the Firewall::Ensure-NetFirewallRule operation that describes what a particular firewall rule should be, or the IIS::Ensure-AppPool and IIS:Ensure-Site operations that define an application environment, each Operation has a set of Parameters that you can specify either visually or code.
See OtterScript & Operations to learn more.
Using PowerShell to Collect Configuration
Otter can also use your existing PowerShell script to verify server configuration. See Compliance as Code with PowerShell & PSVerify to learn more.
Storing Configuration as Code in Git
Although your OtterScript is automatically versioned and backed-up with Otter, you can also use Git repositories.
This is recommended for advanced users, or at least once you've gotten a hang of Otter. See Rafts & Git Storage to learn more.

