HOWTO: Upload Python Packages to a Private PyPI Repository in ProGet
With ProGet you can set up private repositories for your Python packages, so you can publish, store, and share them internally.
This article will run through how to create a "Feed" in ProGet to act as a private Python package repository, as well as covering how to create, publish, and install packages from this feed. This page provides instructions when using pip, however you can also integrate other tools such as PipEnv and Poetry with your PyPI feeds.
Step 1: Create a New Feed
To start with, we will create a feed to host your Python packages. In ProGet, select "Feeds" and "Create New Feed". Then, select "Python Packages" under "Developer Libraries".

Then select "No Connectors (Private packages only)" as we will be creating a private feed. Now name your feed. For this example we will call it internal-pypi.
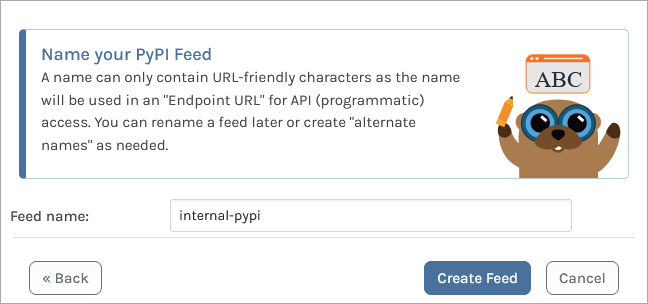
You are then presented with several options. These relate to ProGet's Vulnerability Scanning and Blocking features, however they are only for users looking to use third party packages. Leave these boxes unchecked, and select [Set Feed Features]. You will then be redirected to your new internal-pypi feed, currently empty.
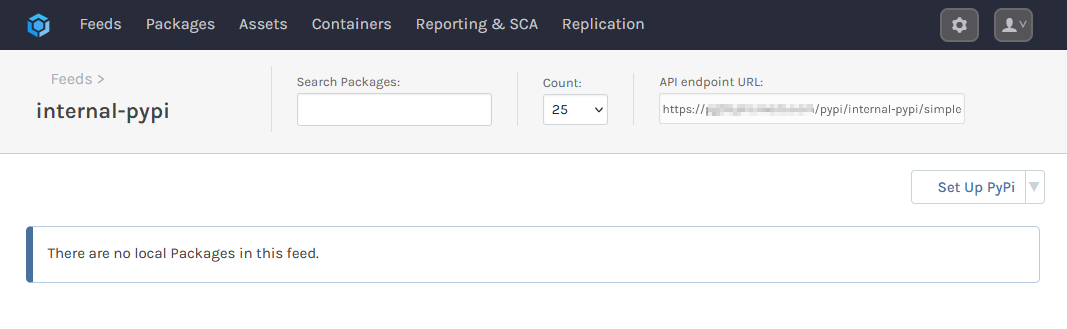
Step 2: Create Your Python Package
Next, we will create our Python packages. You can follow the official Python documentation to learn more about creating these. Before you create a package you will need to have setuptools installed by running pip install setuptools wheel.
To create a Python package you will need a folder with the necessary project files, including setup.py, README.md, and __init__.py. The a project structure will typically look like this:
my_package/
│
├── my_package/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── python_module.py
├── setup.py
├── README.md
Then build your package by navigating to the directory containing setup.py and entering:
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
This will create two directories: dist/ and build/, with .tar.gz (e.g. my_package-1.0.0.tar.gz) and .whl (e.g. my_package-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl)files inside dist/.
For more Best Authoring Practices for Creating Python Packages you can read our article on the Inedo Blog.
Step 3: Create an API Key
Now you will need to create an API Key to let local Python clients authenticate to the internal-pypi feed. This will let you publish and access packages from that feed.
While you can authenticate with a ProGet username and password, we highly recommend using an API Key instead. For that, use api as the username and the API Key as the password.
When creating an API Key, fill in the fields by selecting "Feeds (Use Certain Feeds)" as the "Feed Type" and selecting the internal-pypi feed. Then set the API key. You can use any alphanumeric sequence, or just leave it blank to autogenerate one. Ensure that the "View/Download" and "Add/Repackage" boxes are checked, and then select "Save".
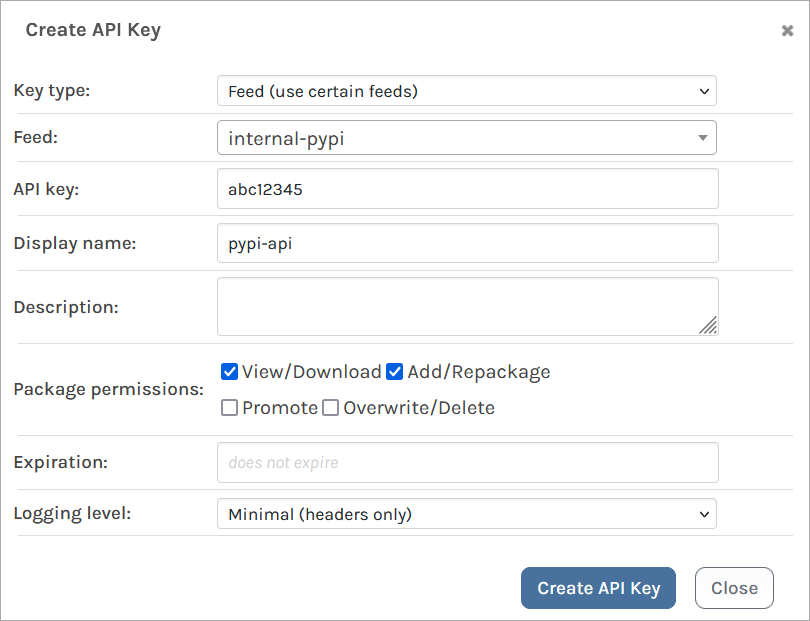
Step 4: Upload Your Package to ProGet
To publish your package to your ProGet internal-pypi feed, you can use pgutil.
pgutil will require some minor configuration before use. This includes setting up your ProGet instance and API key as a source by running:
$ pgutil sources add --name=Default --url=«proget-url» --api-key=«api-key»
Now upload your packages by entering:
$ pgutil packages upload --feed=«feed-name» --input-file=«path-to-package»
To add the ProGet instance https://proget.corp.local/ with the API Key abc12345 you would enter:
$ pgutil sources add --name=Default --url=https://proget.corp.local/ --api-key=abc12345
Then, to upload your package my_package-0.1-py3-none-any.whl stored at C:\development\pypi_packages\my-package\dist to your internal-pypi feed you would enter:
$ pgutil packages upload --feed=internal-pypi --input-file=C:\development\pypi_packages\my-package\dist\my_package-0.1-py3-none-any.whl
Your package will then be uploaded to ProGet:
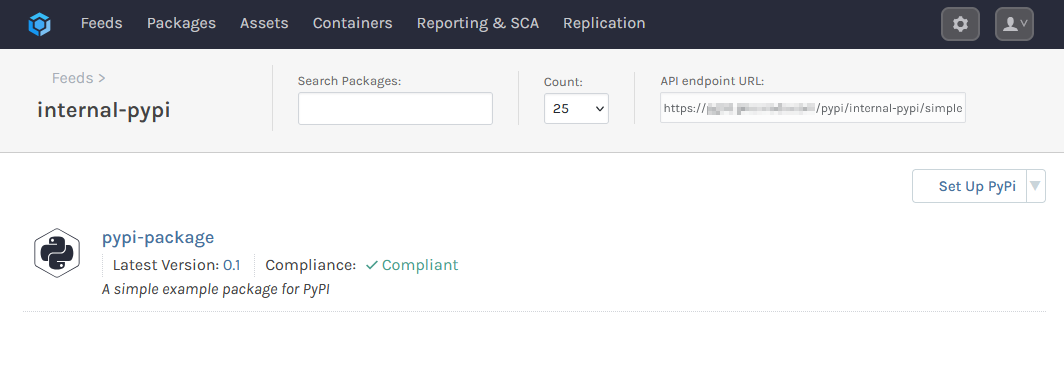
Note that the feed endpoint URLs used when pushing packages vary slightly from the standard feed URL, ending with /legacy rather than /simple
Uploading with Twine
It's also possible to use the twine upload command if want to use twine.
Step 5: Using your PyPI Feed as a Source to Install Packages
To use your internal-pypi feed when installing packages you can either set it globally with the pip config command or run the pip install command. You can also install packages using either PipEnv or Poetry.
Using pip config
Using the pip config command will store your internal-pypi feed in the pip config file, setting it globally as a default source for all package installations. Use the pip config command with a --global parameter containing your feed endpoint URL. For example, when globally setting your internal-pypi package on the ProGet server proget.corp.local you would enter:
$ pip config --global set global.index-url https:/proget.corp.local/pypi/internal-pypi/simple
This command will generate a pip config file that looks like:
[global]
index-url = https:/proget.corp.local/pypi/internal-pypi/simple
Then you can install packages simply using the pip install command:
pip install «package-name»==«package-version»
The pip config can be scoped to global (--global), user (--user), and to the environment (--site). The commands above are scoped to the global scope.
Installing with pip install
You can also use pip install for one-time package installations. Note that as it is not persistent, you'll need to enter your internal-pypi feed URL every time you install a PyPI package, which is why it's recommended that you store your feed in the pip config file using pip config.
To install Python packages with the URL in the pip install command, you will need to add a --extra-index-url parameter containing your feed endpoint URL. For example, when installing my_package 1.0.0 from your internal-pypi package on the ProGet server proget.corp.local you would enter:
$ pip install my_package==1.0.0 --extra-index-url https://proget.corp.local/pypi/internal-pypi/simple
(Optional) Authenticating to the PyPI Feed
By default, your internal-pypi feed can be viewed and installed from anonymously. However, if you have set up authentication for your feed, you authenticate to it by configuring your pip config file with pip config, or by using the pip install command. You also have the option to authenticate using PipEnv or Poetry. As with authenticating when publishing to a feed, we highly recommend Creating a ProGet API Key for authentication, where api is the username and the API key is the password.

