HOWTO: Proxy Packages from the npm Registry in ProGet
With ProGet you can create "Feeds" to proxy packages from the npm Registry (www.npmjs.com) and install them just as you would when installing them from the npm Registry directly.
Using ProGet as a proxy will cache packages, allowing teams to access them even if the npm Registry is down. ProGet will also let you audit packages and assess any vulnerabilities, as well as tell you which packages are being downloaded and used frequently.
This guide will cover how to set up a feed to proxy packages. We'll also cover how to create a private registry for your internal packages as an alternative to the npm Registry's paid private repositories (npm Teams/npm Pro).
Step 1: Create a New Feed
First, we will create an npm feed that will proxy packages from the www.npmjs.com.
Start by selecting "Feeds" and "Create New Feed". Next, select "npm Packages", as we will be creating feeds to proxy and host npm packages.

Now select "Free/Open Source npm Packages" which will allow us to proxy packages from the npm Registry.
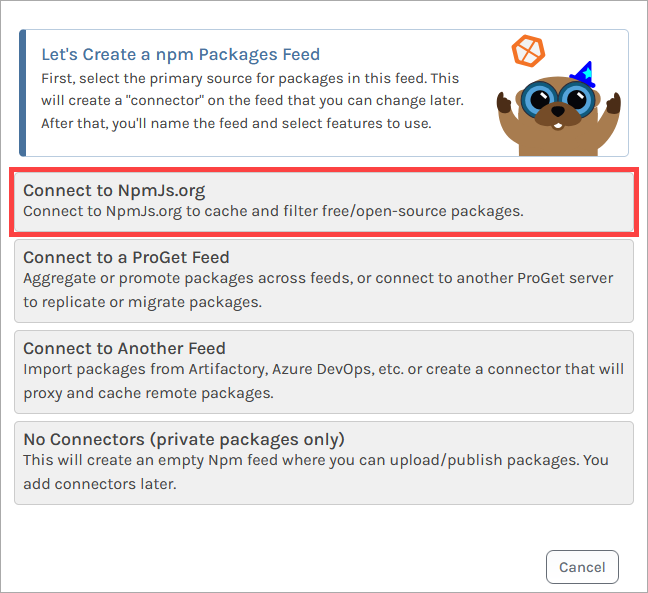
From here, name your feed. In this case, we'll call ours public-npm. Then select "Create New Feed".
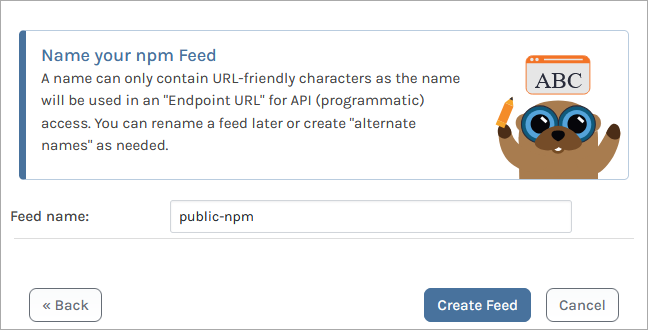
ProGet will then redirect you to the newly created public-npm feed. Currently, npm needs a search term to return package results, so you will need to search for specific packages you need.
Step 2: Add the Feed to npm Clients
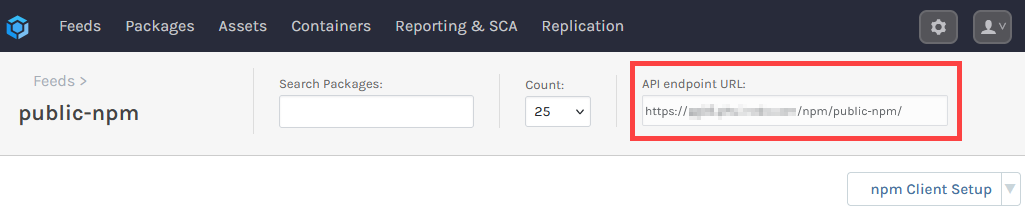
For your team to install packages from the public-npm feed, you'll need to add it as a source in their npm clients. For this, you will need feed's URL. This can be found at the top right of the feed's page.
Now configure your npm client with your public-npm feed with npm config:
$ npm config set registry http://«proget-url»/npm/«feed-name»
Or using yarn with yarn config:
$ yarn config set registry http://«proget-url»/npm/«feed-name»
You can confirm that the feed has been set correctly by using npm get registry for npm, yarn config get registry for Yarn.
Step 3: (Optional) Authenticating to Your npm Feed
By default your public-npm feed does not require authentication and can be viewed anonymously. However, you may want to make your feed private and require authentication to access. Authentication is done by creating an _auth token and then configuring it in your npm client.
(Optional) Auditing npm Packages
If you enabled "Scan for Security Vulnerabilities" when you created a feed you can use npm-audit to scan for vulnerabilities in packages by simply running either npm audit or yarn audit.
Using npm audit with Vulnerability Scanning and Blocking, lets you assess vulnerabilities in packages, and how they impact your organization.
You can also set up Policies & Compliance Rules to create rules for vulnerabilities, licenses, deprecated packages, etc. Setting these up lets you block any packages that are considered "noncompliant".
(Optional) Creating a Package Approval Flow
In this guide we looked at proxying packages from the npm Registry. However, with no form of approval, developers will be able to install any OSS packages without oversight. In many cases, it's important to include some form of oversight in development or production, which can be done by creating a "Package Approval Flow".
To set up a package approval flow, refer to HOWTO: Approve and Promote Open-source Packages. This guide uses NuGet feeds as an example, but the steps are identical when creating npm package feeds.
After creating your "Unapproved" and "Approved" feeds, follow the steps in "Add the Feed to npm Cients" to add the "Approved" feed (e.g. npm-approved) as a source in your npm client using npm config:
$ npm config set registry http://«proget-url»/npm/npm-approved
Or in Yarn with yarn config:
$ yarn config set registry http://«proget-url»/npm/npm-approved

