Resource Monitors & Scheduled Jobs
Resource Monitors have a wide variety of uses in BuildMaster, including:
- Creating a build when a pull request on a Git feature branches is open
- Importing from a Jenkins server) when a successful Jenkins build has a custom parameter named
RELEASE_CANDIDATEset toTRUE - Running an OtterScript when a change is detected in a Subversion repository
There are three aspects to a resource monitor:
- Resource to monitor, such as a Git Repo, SVN repo, CI Project, etc.
- Filter for the monitored resource, like Git branch or CI parameters
- Action to perform when change is detected; there are four options
- Create a build using a release,
- Create a build using a pipeline
- Create a build with a script
- Execute a custom script
Scheduled Jobs work similarly, but instead of monitoring a resource, they simply perform an action at a specified interval, e.g., "Run a nightly build every day at 2:00 AM."
Creating a Resource Monitor
Resource monitors can be configured under Application > Settings.
Depending on the extensions you have installed, you will see different options available. Common ones include:
- Git Repository Monitors; monitors one or many branches in a Git repository for new commits, and optionally filters if there is an open pull request. You can also create/edit by clicking the ⚡icon next to the branch name, on the Branches page.
- CI Project Monitor; monitors a CI project) for new builds, and optionally filters by status (e.g.
SUCCCESS) and custom parameters (RELEASE_CANDIDATE). You can also create/edit by clicking the ⚡icon on the CI Builds page. - Subversion; monitors a path within a Subversion Repository for a new revision number
Note that GitLab & GitHub Webhook Monitors will also be displayed when you click add monitor. These are considered legacy features, and we do not recommend using them.
Scheduled Jobs
Scheduled Jobs can also be configured under Application > Settings.
There are four options for scheduling recurring jobs:
- Every day; specify the time to run
- Weekly; specify the weekday(s) and the time to run
- Monthly; specify the day of the month and the time to run
- Custom; specify a cron expression
Custom schedules are defined with a Quartz-flavored cron expression. These can be complex (see cron expression syntax), but if you search online for "cron expression generators" you may find a tool that matches your needs. For example: https://freeformatter.com/cron-expression-generator-quartz.html
Action: Create Build Using a Release
This action is used to create new builds in a releases, as well as create new releases.
Git Repositories & CI Projects
Releases can be associated with a branch in a Git repository or a CI project. When monitoring these resource types, BuildMaster will only create a new build if a change is detected in this context.
For example, if Release 8.0.0 is associated with master, then new commits to master would trigger a new build of Release 8.0.0. However, commits to develop would not create a new build of 8.0.0.
Other Resource Types
For Subversion, Scheduled Jobs, and other Resource Monitors, BuildMaster will create a new build in all active releases.
Creating a New Release
BuildMaster can also create a new release if one doesn't exist. For example, if you're monitoring a branch named releases/5.2, then you could check the "Create release if it does not exist" option, enter 5.2.* for the release number, and select a pipeline that the release will use.
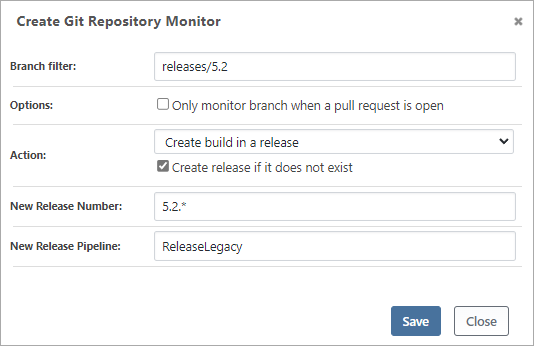
This is particularly useful for building and deploying infrequently released applications.
Action: Create Build Using a Pipeline
This action is used to create new builds in a pipeline, but without using a release. This option is useful if you're not using releases, or if you wish to choose a release later.
The Pipeline filter is used to locate a useable pipeline when creating the build. You can also specify a wildcard expression that ends with *. For example:
Releasewill create a build using a pipeline named Release, or raise an error if one isn't foundDev*will create a build using the first pipeline that starts with Dev
You can specify *, but it's not recommended.
Action: Create build with a Script
This action is used to create new builds in an application using a build script without a pipeline or release. This option is useful when creating disposable builds that execute code compilation, static code analysis, automated unit tests, and so on.
The "Script to run" is the name of the script whose execution you want the Resource Monitor to trigger. This can be an OtterScript or any other type of script that should be executed.
The "Server to use" works like a deployment target for a single server. If you wish to use more advanced server targeting, you can specify localhost, and then use for server and foreach server statements within your script.
Action: Execute Custom Script
When a custom script is selected, that script is run instead of automatically creating a new build. This allows for advanced scenarios, such as creating multiple builds for multiple releases or across multiple applications.
Depending on the resource being monitored, the following variables are available to the custom script.
| Resource | Custom Script Variables Available |
|---|---|
| Git Repository | $Branch and $Commit |
| CI Project | $CIProject and $CIBuildId |
| Subversion | $RevisionNumber |
Advanced: Global Resource Monitors
Global resource monitors give users the ability to monitor global resources for updates. These are typically used in conjunction with executing custom scripts to determine which application to create a new build for.
Global resource monitors can only monitor global resources.
Advanced: Routine Monitoring Operation
When a Git or CI project connection is added to an application, BuildMaster monitors these connections by periodically checking for updates. The update can be run manually by navigating to Administration > Manage Service and clicking the Run link to the right of Repository Monitor. The output of this execution will be shown in the service output.
Once a connection has been checked for updates, the status of the connection is displayed on the application's settings page. If a connection is in an error state, a more detailed message can be viewed by hovering over the error label.
Git Connections
Git connections are synchronized locally with the BuildMaster server. Once synchronization is complete, the repository is checked once per minute by fetching commits from all remote branches. The state of the repository is stored in a local cache file, which is stored in the temporary path of the Git repository.
The temporary path for a repository is displayed on the connection details page. You can view these details by navigating to the application's settings page and clicking the Git connection name.
CI Project Connections
CI projects are queried once per minute by making lightweight calls to the CI server's API. These calls query the API for the latest builds and store them in the database along with a connection state for the CI project.
Troubleshooting
Not seeing latest commit or revision for a branch
Behind the scenes, repository monitors check for new commits/revisions every 4 minutes. If needed, you can check by clicking the Refresh icon on the monitors page. If you don't see the latest commit/revision for a particular branch, check the following:
- verify that the BuildMaster service is running
- attempt to trigger the
Repository Monitortask runner on the Manage Service page and look for live error logs
Logs
Although historical logs are not recorded for repository monitors because they are run very frequently, you can access the Diagnostics Center on the Administration page to view any errors that occurred during the last run of a repository monitor. If no logs were recorded (or no errors were generated), you can also go to the Manage Service page and run the Repository Monitor task runner directly to view all live log output.

