Build Maven Project
A script template is a simple, no-code solution for performing common build or deployment operations and can be converted to OtterScript at any time.
The Build Maven Project Script Template will:
- check out code from Git
- set the project version
- configure repositories (settings.xml)
- optionally build an npm based front-end
- run maven
- capture build artifacts for later deployment
This article will detail the options for these steps, as well as how they're performed.
Using This Script Template
A synchronized Git repository is required for this template, and if your application does not have one, you will not be able to add or edit this script template.
To add this script template to your application, navigate to Scripts, click Add Script, and then select Build Maven Project from the list of Build Script Templates. After doing so, you'll see a dialog like this:
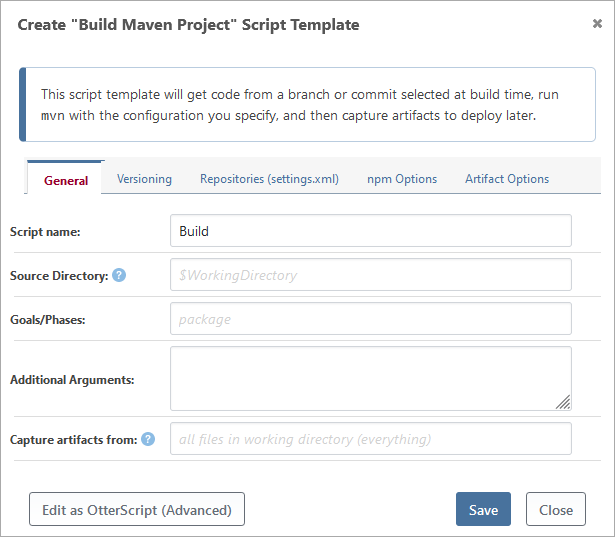
There are a lot of options available, and this article will discuss how these options are used in different steps of the build process.
Note that the Maven and the appropriate JDK is required on the server you'll run this script on (i.e. your build server).
Checking Out from Git
First, the script template checks out code from a Git repository. The branch (or specific commit) is selected when the build is created, before the script is even run. The script will then check out code from that exact commit.
This step uses the Git::Checkout-Code operation without any parameters.
Setting the Project Version
When "Set project version" is checked, the script template will run mvn with the version:set goal and a newVersion argument. This goal and argument will instruct the Versions Maven Plugin to adjust all pom versions, parent versions, and dependency versions in a multi-module project.
This step uses the Java::Maven operation to run mvn versions:set -DnewVersion=«version».
Configuring Repositories (settings.xml)
Maven's settings.xml is generally used to specify the private repositories used for dependencies and plugins. Instead of using the settings.xml file on your build server, BuildMaster can manage these settings for you.
There are four options you can select on the "Repositories" tab:
Do not specify (use global defaults on server)
When selected, you'll BuildMaster will neither generate nor specify a path to a custom settings.xml file. As such, maven will use the default settings.xml on the build server.
Generate based on Maven feeds in ProGet
This option requires a ProGet connection, which you can add under Administration > ProGet Integration.
When selected, you'll be prompted to select a Dependencies Feed and a Plugins Feed from a list of Maven feeds in ProGet. Prior to executing maven, BuildMaster will generate a settings.xml file with URLS and credentials (i.e. API Key) that may be required to access these feeds.
Use a Text Template Script Asset
This option allows you to store a settings.xml file inside of BuildMaster as a text template script asset so that you can do variable replacement or advanced conditional logic.
When selected, you'll be prompted to enter the name of a text template that you've added to BuildMaster. Prior to executing Maven, BuildMaster will write that file to disk and instruct Maven to use it.
Selecting a Text Template will add the InedoCore::Apply-Template operation prior to Java::Maven.
Specify custom file path
This option allows you to enter a path (relative to $WorkingDirectory). BuildMaster simply pass this as the -s argument to Maven, which will instruct Maven to use that file instead of the default.
Building npm Front-Ends
When a Maven web application uses npm to build or enhance their front-end pages, there is an option to enable building an npm project on the "npm Options" tab. Once enabled, the script template will set an npm version (optional), install npm packages (npm install), and run the build script (npm run build).
When enabled, the the script template will add the following operations to the script:
npm:Set=ProjectVersion(optional)npm::Installnpm::Build
npm Package Source
Select where to fetch the npm packages needed to build your project. This list will typically contain npm feeds from your connected ProGet instance, and an option for Not Specified, which will use the public npmjs.com repository. When a ProGet feed is selected, a temporary .npmrc will be created in the Source Directory and will pass a --userconfig= to npm install command.
Allow ProGet feeds using a Self-Signed certificate
When npm handles certificate validation, it will use an internal certificate source. This will error when using invalid certificates like self-signed and internal CA generated certificates even if they are trusted in the Widnows certificate manage. If ProGet is configured to use a self-signed or internal CA generated certificate, you will need to bypass npm's certificate validate by checking the "Allow ProGet feeds using a Self-Signed certificate" option.
Source Directory
Enter the source directory for where the package.json can be found. By default, the script template will search your git repository, when connected, for the package.json and pre-populate the path. If a package.json is not found, the default value is $WorkingDirectory.
Additional Build Arguments
When specified, these arguments will be passed to the npm::Build operation with the AdditionalArguments parameter. When the npm::Build operation is ran, these are then passed directly to the npm run build commmand.
Project Version
This sets project version for the npm project. The default value is to not update the vesion, but you have the choice to use the project version you specified for your maven application or the enter a custom version number for your project.
When this option is selected, the npm::Set-ProjectVersion will be run with the Version parameter.
Running Maven
Next, the script template will run mvn with arguments based on what you've entered in the template. None of the arguments will be quoted; they're simply appended as raw values as follows:
mvn «goals-and-phases» «additional-arguments» -s «settings-xml-option»
If "Do not specify" is the selected Settings.xml option, then the -s «settings-xml-option» will not be appended to the arguments.
This step uses the Java::Maven operation. The parameters will depend on the options you've entered.
Running Maven Using a Docker Container
By default, Maven projects will built by executing the maven «goals-and-phases» ... command in a working directory on a target server. However, if you've enabled BuildMaster's Image-based Services feature, you can configure Maven projects to build inside of a Docker container instead.
To do this, select the "Docker" tab, check "Run in container" and then select the image you would like to use to build your Maven project. You can add or customize the images in this list under Admin > Image-based Services. When selected, the script will function mostly the same, except maven «goals-and-phases» ... will be executed in the container using the working directory as a mounted volume.
This option adds the ImageBasedService parameter to the Java::Maven operation with the selected value.
Capturing Build Artifacts
As the last step, BuildMaster will capture artifacts from a path within the working directory that you specify. These are the files that you will deploy later.
The specific path within the working directory can be difficult to predict, and it may take a few builds for you to find the path you'd like to capture.
Finding the Right Subpath
Usually, the easiest way to find the path you want is:
- Create a build using this template
- Inspect the build's artifacts
- Find the subpath you want within the artifact
- Enter that in the "Capture artifacts from:"
Then, the build artifact going forward will contain only those files.
This step uses the Create-Artifact operation, with the parameters depending on the options you've entered.

