Vulnerability Scanning & Blocking
ProGet can automatically scan third-party open-source packages and container images for vulnerabilities, allowing you to assess the risk they may pose. This allows you to not only block packages or container images that you deem too risky for use, but also determine which of your Projects and Releases are affected by security vulnerabilities. You can also warn users about security vulnerabilities and receive alerts when new vulnerabilities are discovered.
For a walkthrough on how to configure vulnerability scanning in just a few minutes, see HOWTO: Scan and Block Packages in ProGet.
This article explains how vulnerability scanning works and how you can configure blocking rules and assessments when a package is found to be vulnerable.
Package Vulnerabilities
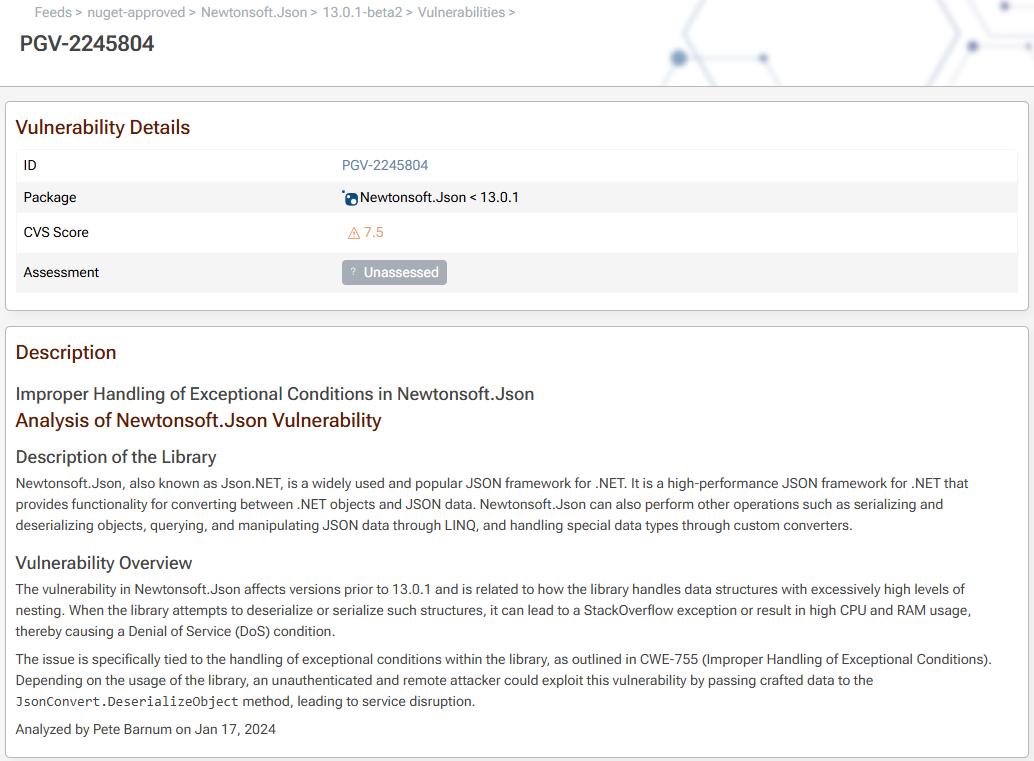
When the "vulnerability detection" feature is enabled on your feed, a "Vulnerabilities" tab will appear on packages and list the known vulnerabilities that were detected. Clicking on a vulnerability will provide information about the severity, reproduction details, remediation steps, and so on.
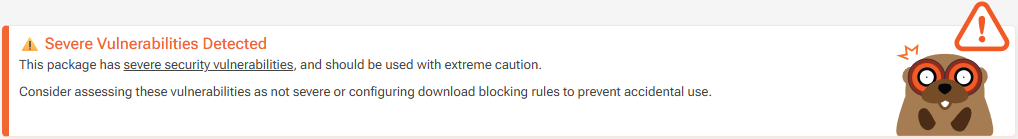
When a package has a severe vulnerability, you’ll see this message on the overview page:
Blocking Vulnerable packages
If you have a paid version of ProGet, you'll be able to configure blocking rules so that packages like this can't be downloaded as well as assess vulnerabilities and comment as to why they're severe or okay for your organization.
Package blocking is configured on a feed-by-feed basis under SCA & Reporting > Vulnerabilities. When enabled on a feed, users will not be able to download blocked packages from the UI or use the API.
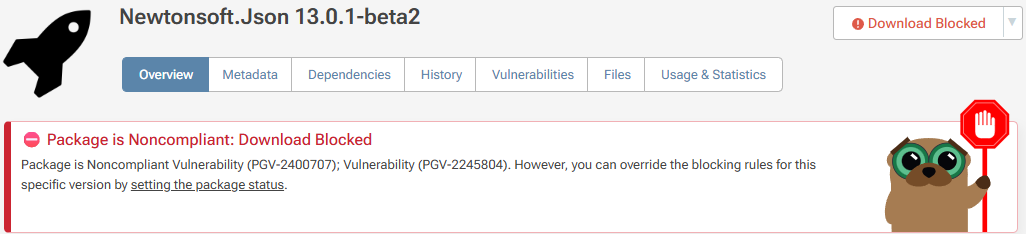
Attempts to download the package from the API will result in a "404" error.
A package will be blocked when:
- A vulnerability was assessed as severe enough to prevent downloads
- The vulnerability is unassessed, and you enabled the "block unassessed" rule on the feed.
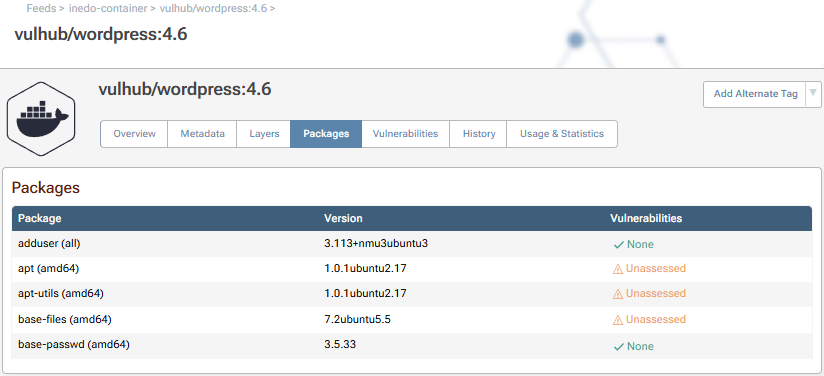
Container Vulnerabilities
To scan containers for vulnerabilities, ProGet extracts and inspect the files within each container image layer and looks for vulnerable packages that are installed. The "Packages" and "Vulnerabilities" tab of a container image will show these:
This feature requires ProGet 2023.29 or later; older versions of ProGet integrate with a free, open-source tool to extract and inspect the layers. See HOWTO: Integrate Clair and ProGet to learn how to configure this tool.
Assessing Vulnerabilities
Many vulnerabilities – even severe ones – will not have an impact on your applications.
For example, consider the vulnerability on the Newtonsoft.Json package in the screenshots above: Improper Handling of Exceptional Conditions in Newtonsoft.Json.
If you read the details of the vulnerability, you’ll see that applications that use that version of the package will be susceptible to a Denial of Attack if a malicious user is able to send a massive (9.5MB+) JSON request to an API.
For public-facing applications, that’s a pretty big deal – and an anonymous hacker could quickly disrupt your service. But for internal-use applications, these attacks are highly unlikely. Not only that, you can easily bypass the vulnerability by checking the size of the JSON request, setting a recursion limit in the Newtonsoft configuration, etc.
This is where vulnerability assessments come in: authorized users can assess these vulnerabilities, select an assessment type (Ignore, Caution, Block, etc.), and leave an optional comment explaining the decision.
Assessment Expiration
Vulnerability assessments can expire. When an assessment expires, the vulnerability will be considered "unassessed" and may cause the package download to be blocked, depending on whether unassessed vulnerabilities are allowed on the feed.
This is primarily useful to temporarily allow packages. For example, you could temporarily allow Newtonsoft.Json 12.0.3 for 90 days by assessing it as "Caution"; once the assessment expires (and the feed is configured to block unassessed packages), the package will no longer be downloadable.
Assessment Types
ProGet has three built-in assessment types:
- Ignore indicates that the vulnerability report is not applicable or irrelevant and therefore allows packages to be downloaded
- Caution tells developers to be careful to avoid the vulnerability; packages can be downloaded, but a warning is issued on the web UI
- Blocked means that a vulnerability is too severe to allow use and packages cannot be downloaded
You can edit these types or create your own by going to "Admin Overview" > "Assessment Types" and clicking on "Create Assessment Type" to specify a name, expiration (days), color, whether or not to block packages, and an area for automatic assessment.
Auto assessment can be customized to your preferences. However if you’re unsure of what the best option is; we recommend the following auto-assessment setup:
| Assessment Type | Auto assess (CVSS) | Expiration |
|---|---|---|
| Ignore | Low (0.1-3.9) | 90 days |
| Caution | High (7.0-8.9) | 30 days |
| Blocked | Critical (9.0-10.0) | 30 days |
This configuration will ignore low score vulnerabilities that typically will not impact your security while critical vulnerabilities are immediately blocked for download.
Medium score vulnerabilities will be left unassessed in this case because these vulnerabilities should be reviewed by someone to determine if they are ignored, require caution, or—in rare cases—should be blocked. These medium-score vulnerabilities do not typically require immediate action.
High score vulnerabilities are not blocked in this scenario—but should be treated with caution because they typically have a security flaw in a specific feature of the package, but may not be a feature that your application is leveraging.
Assessment Scores
Most vulnerabilities will have a simple "score" that rates the severity on a scale of 0.1 to 10.0 using a variety of factors. You can automatically assess vulnerabilities based on this score to either:
- Ignore or warn about low-score vulnerabilities
- Block high-score vulnerabilities
Auto-assessment rules will also not be applied to vulnerabilities with an expired assessment.
Custom Vulnerability types
Creating and using custom vulnerability types can be very helpful when:
- You want different vulnerability expirations
- You want to tag vulnerabilities that may be treated or reviewed differently
For example: Let's say you want an auto assessment for high (7.0-8.9) to not block, but they require a critical review. To accomplish this, you could create a "Critical Review" assessment type that auto-assesses when a high vulnerability is located. Then a security admin can filter these on the Vulnerabilities page in ProGet to do critical reviews.
ProGet 2023 and earlier
ProGet 2023 and earlier behave very similar to what's documented, but there are a few minor behavioral and configuration changes to be aware of.
Vulnerability Assessments
In ProGet 2023, existing vulnerabilities that were already added to ProGet will not be auto-assessed. This means that, when you configure auto-assess on an assessment type, it will only apply to new, unassessed vulnerabilities.
In addition, ProGet 2023 vulnerability assessments do not have their own expiry date. Instead, it is calculated based on the expiry rule on an assessment type. This means that, when you edit the expiry rule field, it will apply immediately to all vulnerabilities assessed with that type. Depending on when the vulnerability was assessed, it may immediately expire or be valid.
Assessment Types & Blocked Packages
In ProGet 2023, Assessment Types have a "Block Packages" option. When this option is selected, packages that have vulnerabilities that were assessed with this assessment type will be blocked.
Manual Vulnerability Records
ProGet 2023 and earlier allows you to add a manual vulnerability record on a specific package version (or version ranges), or on a container image layer. These are used almost exclusively as a "hack" to block downloads of certain packages, are have since been discontinued in ProGet 2024 favor of other tools to prevent usage of noncompliant packages.
To add manual records, navigate to the Vulnerabilities tab on the package or container image page then click the Add Vulnerability button to specify the feed, the package ID, and version(s) or the container image layer digest, and the details of the vulnerability.
Manual vulnerability records may encompass multiple package versions using version range syntax, for example:
| Range | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 3.0.0 | version = 3.0.0 |
| [3.0] | version = 3.0 |
| <=2.0 | version <= 2.0 |
| [1.3,1.4] | 1.3 <= version <= 1.4 |
| >=1.3 <=1.4 | 1.3 <= version <= 1.4 |
| >2.5 | version > 2.5 |
| <=1.0,>=1.2 | version <= 1.0 or version >= 1.2 |
| <1.1 >1.1 | Exclude version 1.1 |
| [, 2.0.0] | version >= 2.0.0 and < 3.0.0 |
Note: versions must be specified out to their full value to match. For example, 2.0 will not match 2.0.0
Due to the inconsistency in container repository tags, container registries are not compatible with version ranges.
Vulnerability Sources
ProGet 2023 and earlier uses a component called "Vulnerability Sources" to scan packages. You can configure these on Admin > Vulnerability Sources, and we recommend using only one vulnerability source at a time.
ProGet Vulnerability Central (PGVC)
ProGet Vulnerability Central (PGVC) is uses a database from Inedo Security Labs, which is includes an industry-leading aggregation of publicly-disclosed vulnerabilities from a variety of sources, as well as malicious packages we've detected.
It's bundled as an offline database in ProGet and is used to show which open-source packages have which vulnerabilities. In most cases, PGVC will be enabled by default. If you enabled OSS Index in ProGet 2022 or earlier, it will be disabled.
Third-Party Vulnerability Sources
In addition to PGVC, ProGet 2023 and earlier also supports the use of third-party vulnerability sources such as OSS Index. ProGet runs a recurring job to scan your local (or Connector cached) packages. Note that remote Connector packages that are not cached locally cannot be scanned using a third-party vulnerability source, since ProGet must submit a list of all packages and versions to be queried, and this information is often not available from remote sources.
Information about vulnerabilities from a third-party source is not displayed on the Vulnerabilities tab unless the package is cached or otherwise stored locally and the nightly scan job has been run.
Malicious Packages
This section refers to newer versions of ProGet only; see Changes to Malicious Package Handling in 2025.20 and Beyond to learn more.
ProGet will also detect and automatically block known Malicious Packages.
Unlike a package with unintentional vulnerabilities (defects) that may open your applications to security exploits if used in a certain way, a malicious package is always unsafe to use because it was intentionally crafted to cause harm. As such, this blocking is automatic and cannot be configured.
In the unlikely event you need to override this behavior, you will need to:
- Acquire a copy of the package file
- Publish it to the feed
- Set the Package Status to "Always Allow Download"
Malicious Package Database
ProGet is installed with a malicious package database that contains the names/versions of hundreds of thousands of known packages.
By default, this database is updated on a nightly basis by downloading an update from Inedo Security Labs. You can see the status of the database under Admin > Vulnerabilities & Assessment Types > Databases
Malicious Packages & Compliance
A malicious package is always considered noncompliant. In the unlikely event you'd want to override this behavior, you can work-around this behavior by publish a copy of the package to a feed and setting the Package Status to "Always Allow Download".
This means that:
- if a malicious package is included in a Build, the build will always be considered noncompliant
- if a malicious package is found in a feed, it will trigger notifiers as appropriate

