ASP.NET MVC & WebForms
BuildMaster can help build and deploy your ASP.NET MVC or WebForms applications to Windows (IIS), Linux, and the cloud.
ASP.NET MVC is the most popular web framework for .NET, allowing developers to create maintainable, scalable, and cross-platform web applications. By separating the concerns (i.e., not coupling the HTML views with the database backend and vice versa), teams of developers with different skill sets can focus on their areas of expertise without having to understand the intimate details of the underlying framework as they did with its predecessor, ASP.NET WebForms.
This article will walk through how to automate the build and deployment of an ASP.NET web application.
CI/CD for ASP.NET Web Applications
The best way to build and deploy your ASP.NET Web Applications is with an automated, repeatable process (i.e. a pipeline).
BuildMaster includes several pipeline templates, and you can customize one to follow your current or desired process
The standard, three-environment pipeline is common in most organizations, but you can add and remove stages as needed.
Creating a Build Script for ASP.NET Web Applications
The general process for building an ASP.NET application is as follows:
- Get source code from the source control repository
- Compile project with MSBuild or
dotnet publish - Capture artifact for deployment
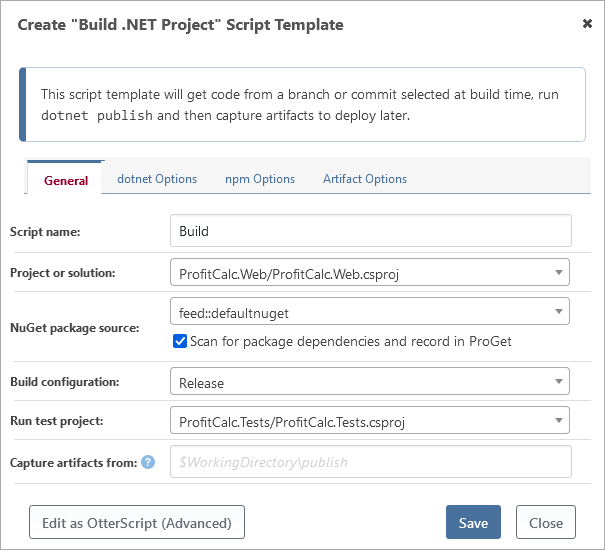
Using BuildMaster's Build .NET Project Script Template
BuildMaster includes a number of script templates that offer a simple, no-code solution for performing common build or deployment operations and can be converted to OtterScript to allow more advanced solutions. The Build .NET Project Script Template contains the most common operations needed to pull the source code, build, test (optional), and create an artifact of your ASP.NET application.
Using OtterScript Directly
Compiling a ASP.NET Application
To build an ASP.NET application, the first step is to acquire the source code from your SCM of choice, e.g. using Git::Get-Source. Once the source code is obtained, simply run the MSBuild::Build-Project or the DotNet::Publish operation.
Using dotnet publish for .NET 5+
For .NET 5+, the dotnet cli is included in .NET SDK. This will contain the components to build a .NET application, but may be missing any extra third-party dependencies. If you are on Windows, you can install the .NET SDK and any dependencies you may need using the Visual Studio Build Tools. For other operating systems, you will need to install these dependencies manually.
A rough example plan of this would be:
Git::Get-Source
(
RepositoryUrl: https://github.com/Inedo/ProfitCalc.git,
Branch: master
);
DotNet::Publish ProfitCalc.Web\ProfitCalc.Web.csproj
(
Configuration: Release,
Output: ~\Output
);
Create-Artifact
(
From: ~\Output\_PublishedWebsites\ProfitCalc.Web
);
The DotNet::Publish operation in this example effectively runs the following dotnet publish command:
dotnet publish ProfitCalc.Web\ProfitCalc.Web.csproj -c Release -o "C:\...<buildmaster-temp>...\Output\\"
Using MSBuild for .NET Framework
MSBuild doesn't require Visual Studio to be installed, but you will need to install and configure Visual Studio Build Tools. Make sure that ".NET desktop build tools" and "Web development build tools" options are chosen during installation/modification
A rough example plan of this would be:
Git::Get-Source
(
RepositoryUrl: https://github.com/Inedo/ProfitCalc.git,
Branch: master
);
MSBuild::Build-Project ProfitCalc.Web\ProfitCalc.Web.csproj
(
To: ~\Output
);
Create-Artifact
(
From: ~\Output\_PublishedWebsites\ProfitCalc.Web
);
The MSBuild::Build-Project operation in this example effectively runs the following MSBuild command:
msbuild.exe ProfitCalc.Web\ProfitCalc.Web.csproj "/p:Configuration=Release" "/p:OutDir=C:\...<buildmaster-temp>...\Output\\"
Restoring NuGet Packages
By default, MSBuild does not restore NuGet packages during a build, but dotnet publish will. This will often the cause of "are you missing an assembly reference" errors. If you get an error message like this, you will need to use the NuGet::Restore-Packages operation.
An example of the NuGet::Restore-Packages operation is as follows:
NuGet::Restore-Packages
(
Target: ~\Src\<project-name>,
Source: https://proget.corp/nuget/InternalNuGet/
);
This will essentially call nuget.exe install, and instruct it to look for a packages.config file in the SourceDirectory, and packages in the target Source.
Unit Tests
Unit tests for ASP.NET applications are handled by VSTest. An example operation to execute and capture unit test results is as follows:
WindowsSdk::Execute-VSTest
(
TestContainer: ~\Output\ProfitCalc.Tests.dll
);
Creating a Deploy Script for ASP.NET
While ASP.NET applications can be hosted on a variety of web servers, Microsoft's Internet Information Services (IIS) is the most common. See our Deploy IIS Site Script Template or our Deploying an IIS Website to learn how to accomplish this with BuildMaster.

